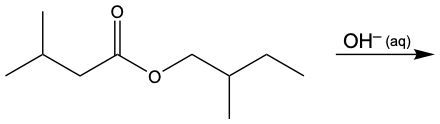
In this video, we're going to take a look at a particular ester reaction called Saponification. Now, under this reaction, the hydroxide ion, so OH-, dissolved in water reacts with an ester. This reaction cuts or cleaves the ester bond to create a carboxylate anion and an alcohol. Now here, what is a carboxylate anion? Well, that's just the conjugate base form of a carboxylic acid, and here we consider this to be the opposite process of esterification.
Now, saponification. Here we have our Ester, and this here represents our Ester linkage. When we use OH- dissolved in water, so aqueous OH-, it's going to cut this bond here, cut this connection. By cutting this connection, this oxygen gains an H to reform our alcohol, and this carbonyl gains an O-, it becomes our carboxylate anion. So remember, the carboxylate anion is the conjugate base of a carboxylic acid. Conjugate base just means we lose an H+. Losing an H+ is why that oxygen now is negatively charged. Right? So keep this in mind when we encounter any type of saponification reaction.