Back
BackProblem 1a
What experimentally derived information led to Holley's proposal of the two-dimensional cloverleaf model of tRNA?
Problem 1b
What experimental information verifies that certain codons in mRNA specify chain termination during translation?
Problem 1c
How do we know, based on studies of Neurospora nutritional mutations, that one gene specifies one enzyme?
Problem 1d
On what basis have we concluded that proteins are the end products of genetic expression?
Problem 1e
How do we know that the structure of a protein is intimately related to the function of that protein?
Problem 2
Write a short essay that discusses the role of ribosomes in the process of translation as it relates to these concepts.
Problem 3
Contrast the roles of tRNA and mRNA during translation, and list all enzymes that participate in the transcription and translation process.
Problem 4
Francis Crick proposed the 'adaptor hypothesis' for the function of tRNA. Why did he choose that description?
Problem 5
During translation, what molecule bears the codon? the anticodon?
Problem 6
The α chain of eukaryotic hemoglobin is composed of 141 amino acids. What is the minimum number of nucleotides in an mRNA coding for this polypeptide chain?
Problem 7
Assuming that each nucleotide in an mRNA is 0.34 nm long, how many triplet codes can simultaneously occupy the space in a ribosome that is 20 nm in diameter?
Problem 8
Summarize the steps involved in charging tRNAs with their appropriate amino acids.
Problem 9
To carry out its role, each transfer RNA requires at least four specific recognition sites that must be inherent in its tertiary structure. What are they?
Problem 10
What are isoaccepting tRNAs? Assuming that there are only 20 different aminoacyl tRNA synthetases but 31 different tRNAs, speculate on parameters that might be used to ensure that each charged tRNA has received the correct amino acid.
Problem 11
When a codon in an mRNA with the sequence 5'-UAA-3' enters the A site of a ribosome, it is not recognized by a tRNA with a complementary anticodon. Why not? What recognizes it instead?
- Discuss the potential difficulties of designing a diet to alleviate the symptoms of phenylketonuria.
Problem 12
- Individuals with phenylketonuria cannot convert phenylalanine to tyrosine. Why don't these individuals exhibit a deficiency of tyrosine?
Problem 13
- Early detection and adherence to a strict dietary regimen have prevented much of the intellectual disability that used to occur in those with phenylketonuria (PKU). Affected individuals now often lead normal lives and have families. For various reasons, such individuals tend to adhere less rigorously to their diet as they get older. Predict the effect that mothers with PKU who neglect their diets might have on newborns.
Problem 14
Problem 15a
The synthesis of flower pigments is known to be dependent on enzymatically controlled biosynthetic pathways. For the crosses shown here, postulate the role of mutant genes and their products in producing the observed phenotypes:
P₁: white strain A × white strain B
F₁: all purple
F₂: 9/16 purple: 7/16 white
Problem 15b
The synthesis of flower pigments is known to be dependent on enzymatically controlled biosynthetic pathways. For the crosses shown here, postulate the role of mutant genes and their products in producing the observed phenotypes:
P₁: white × pink
F₁: all purple
F₂: 9/16 purple: 3/16 pink: 4/16 white
Problem 16
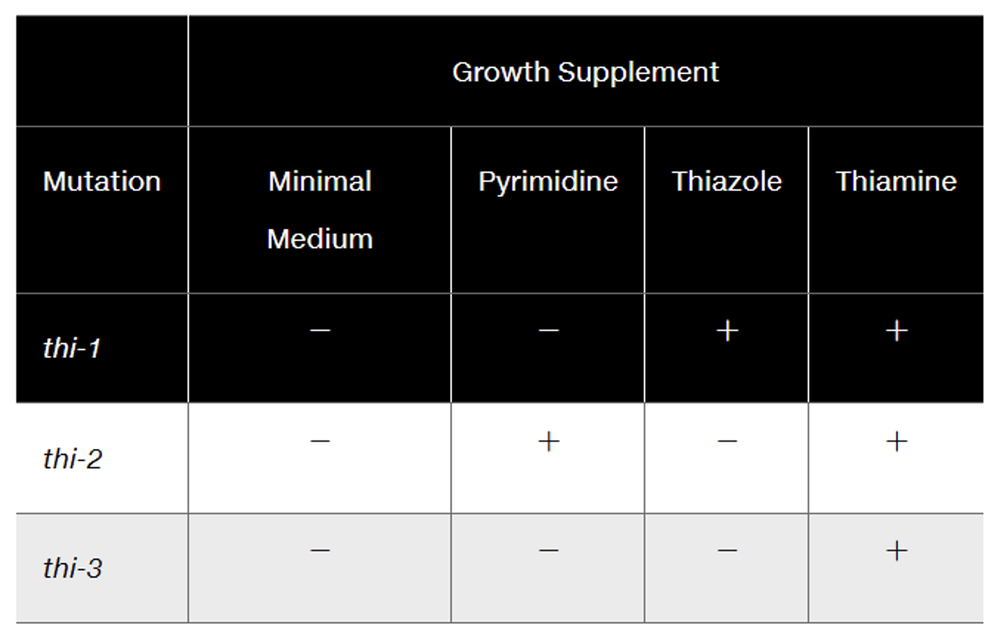
The study of biochemical mutants in organisms such as Neurospora has demonstrated that some pathways are branched. The data shown in the following table illustrate the branched nature of the pathway resulting in the synthesis of thiamine:
Why don't the data support a linear pathway? Can you postulate a pathway for the synthesis of thiamine in Neurospora?
Problem 17
Explain why the one-gene:one-enzyme concept is not considered totally accurate today.
- Why is an alteration of electrophoretic mobility interpreted as a change in the primary structure of the protein under study?
Problem 18
Problem 19
Using sickle-cell anemia as an example, describe what is meant by a molecular or genetic disease. What are the similarities and dissimilarities between this type of a disorder and a disease caused by an invading microorganism?
Problem 20
Contrast the contributions of Pauling and Ingram to our understanding of the genetic basis for sickle-cell anemia.
- Hemoglobins from two individuals are compared by electrophoresis and by fingerprinting. Electrophoresis reveals no difference in migration, but fingerprinting shows an amino acid difference. How is this possible?
Problem 21
Problem 22
HbS results in anemia and resistance to malaria, whereas in those with HbA, the parasite Plasmodium falciparum is able to invade red blood cells and cause malaria. Predict whether those with HbC are likely to be anemic and whether they would be resistant to malaria.
Problem 23
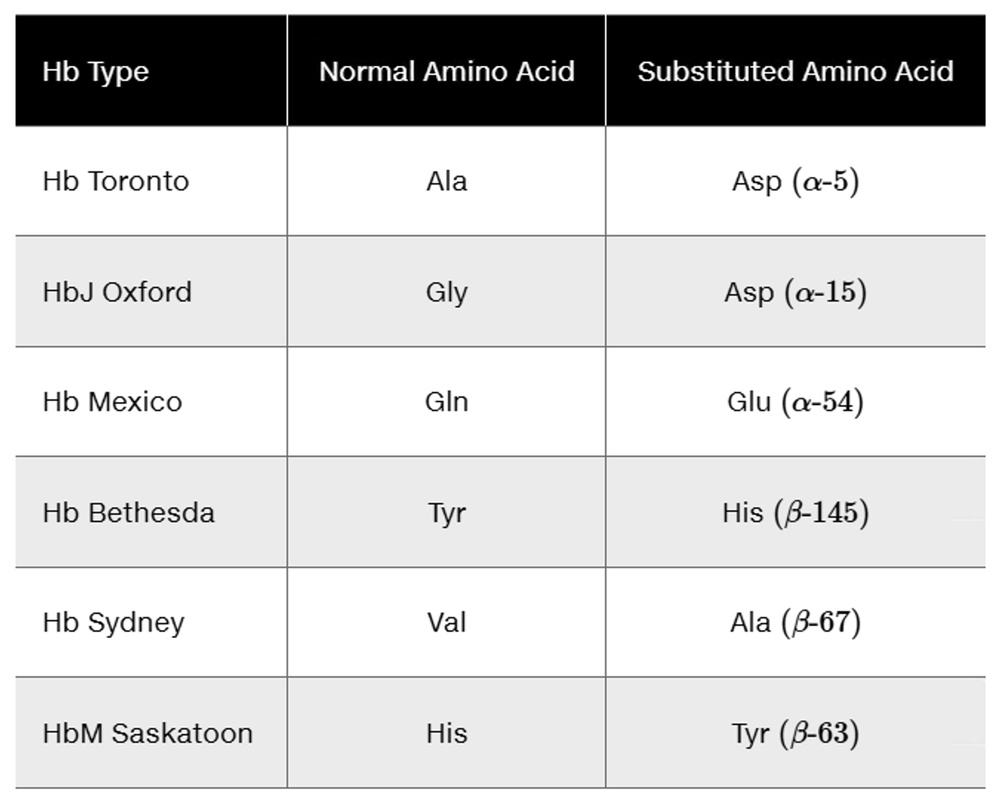
Several amino acid substitutions in the α and β chains of human hemoglobin are shown in the following table.
Using the code table, determine how many of them can occur as a result of a single-nucleotide change.
Problem 24
Define and compare the four levels of protein organization.
Problem 25
What are the two common types of protein secondary structure, and how do they differ?