Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Codons and Amino Acids
Codons are sequences of three nucleotides in mRNA that correspond to specific amino acids during protein synthesis. Each codon is matched to an amino acid based on the genetic code, which is universal across most organisms. Understanding the relationship between codons and their respective amino acids is crucial for interpreting the results of genetic experiments.
Recommended video:
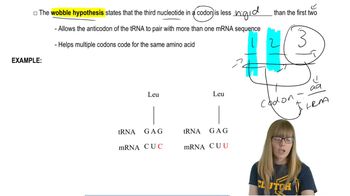
Wobble Hypothesis
The wobble hypothesis explains how the third nucleotide in a codon can vary without affecting the amino acid that is produced. This flexibility allows for some redundancy in the genetic code, where multiple codons can code for the same amino acid. Recognizing this concept is essential for accurately assigning codons to their corresponding amino acids in the context of the experiment.
Recommended video:
Translation:Wobble Hypothesis
Copolymers in Genetic Experiments
Copolymers are polymers made from two or more different monomers, and in genetic experiments, they can be used to study the effects of varying sequences on protein synthesis. By analyzing how different copolymers produce specific codons and amino acids, researchers can gain insights into the mechanisms of translation and the role of sequence variation in protein function.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance