Textbook Question
How do we know that the structure of a protein is intimately related to the function of that protein?
552
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
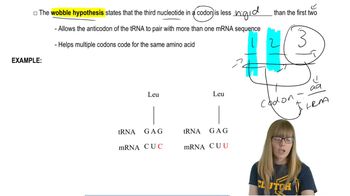


How do we know that the structure of a protein is intimately related to the function of that protein?
Write a short essay that discusses the role of ribosomes in the process of translation as it relates to these concepts.
Contrast the roles of tRNA and mRNA during translation, and list all enzymes that participate in the transcription and translation process.
During translation, what molecule bears the codon? the anticodon?
The α chain of eukaryotic hemoglobin is composed of 141 amino acids. What is the minimum number of nucleotides in an mRNA coding for this polypeptide chain?
Assuming that each nucleotide in an mRNA is 0.34 nm long, how many triplet codes can simultaneously occupy the space in a ribosome that is 20 nm in diameter?