Back
BackProblem 1a
How do we know how methylation of promoters silences gene expression?
Problem 1b
What is the evidence that epigenetic changes are involved in cancer?
Problem 1c
How does an environmental factor like stress generate a response that is transmitted from generation to generation?
Problem 2
Write a short essay describing how epigenetic changes in cancer cells contribute to the development and maintenance of cancers.
Problem 3
What are the major mechanisms of epigenetic genome modification?
Problem 4
What parts of the genome are reversibly methylated? How does this affect gene expression?
Problem 5
Identical twins each carry the same genome, but over time, can develop different phenotypes. How can you explain this?
Problem 6
What are the possible roles of proteins in histone modification?
Problem 7
Describe how reversible chemical changes to DNA and histones are linked to chromatin modification.
Problem 8
Why are changes in nucleosome spacing important in changing gene expression?
Problem 9
What are the similarities and differences in the two types of ncRNAs involved in epigenetic control of gene expression?
Problem 10
How do microRNAs regulate epigenetic mechanisms during development?
Problem 11
What are the functions of lncRNAs in epigenetic regulation? Describe each in detail.
Problem 12
What is the histone code?
Problem 13
What are the differences and similarities among the three classes of monoallelic gene expression?
Problem 14
What is the role of imprinting in human genetic disorders?
Problem 15
Imprinting disorders do not involve changes in DNA sequence, but only the methylated state of the DNA. Does it seem likely that imprinting disorders could be treated by controlling the maternal environment in some way, perhaps by dietary changes?
Problem 16
Should fertility clinics be required by law to disclose that some assisted reproductive technologies (ARTs) can result in epigenetic diseases? How would you and your partner balance the risks of ART with the desire to have a child?
Problem 17
How can the role of epigenetics in cancer be reconciled with the idea that cancer is caused by the accumulation of genetic mutations in tumor-suppressor genes and proto-oncogenes?
Problem 18
How are mutations in histone acetylation (HAT) genes linked to cancer?
Problem 19a
A developmental disorder in humans called spina bifida is a neural tube defect linked to a maternal diet low in folate during pregnancy.
What does this suggest about the cause of spina bifida?
Problem 19b
A developmental disorder in humans called spina bifida is a neural tube defect linked to a maternal diet low in folate during pregnancy.
Does this exclude genetic mutations as a cause of this condition?
Problem 19c
A developmental disorder in humans called spina bifida is a neural tube defect linked to a maternal diet low in folate during pregnancy.
Should researchers be looking for mutant alleles of genes that control formation and differentiation of the neural tube?
Problem 20
Trace the relationship between the methylation status of the glucocorticoid receptor gene and the behavioral response to stress.
Problem 21a
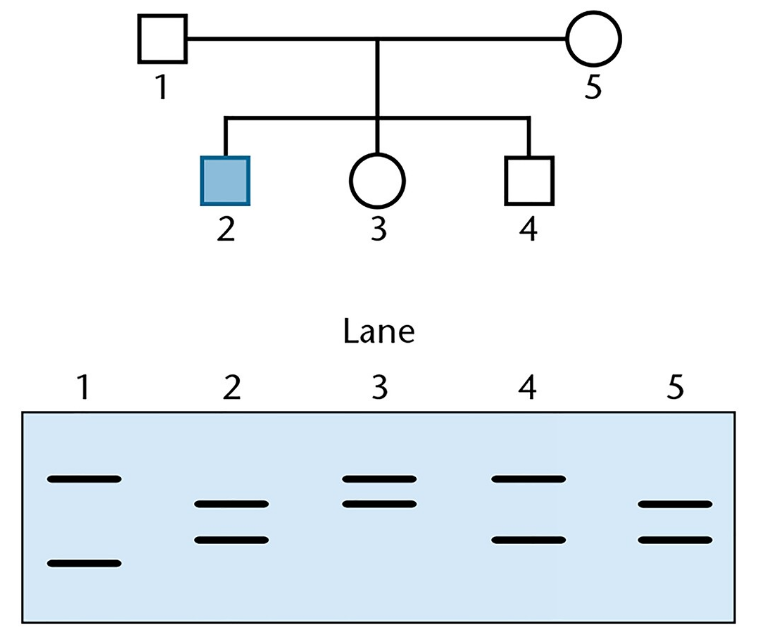
Prader–Willi syndrome (PWS) is a genetic disorder with a clinical profile of obesity, intellectual disability, and short stature. It can be caused in several ways. Most common is a deletion on the paternal copy of chromosome 15, but it can also be caused by an epigenetic imprinting disorder and uniparental disomy, an event in which the affected child receives two copies of the maternal chromosome 15. A child with PWS comes to your clinic for a diagnosis of the molecular basis for this condition. The gel below shows the results of testing with short tandem repeats (STRs) from the region of chromosome 15 associated with the disorder.
Is this case caused by a deletion in the paternal copy of chromosome 15? Explain.
Problem 21b
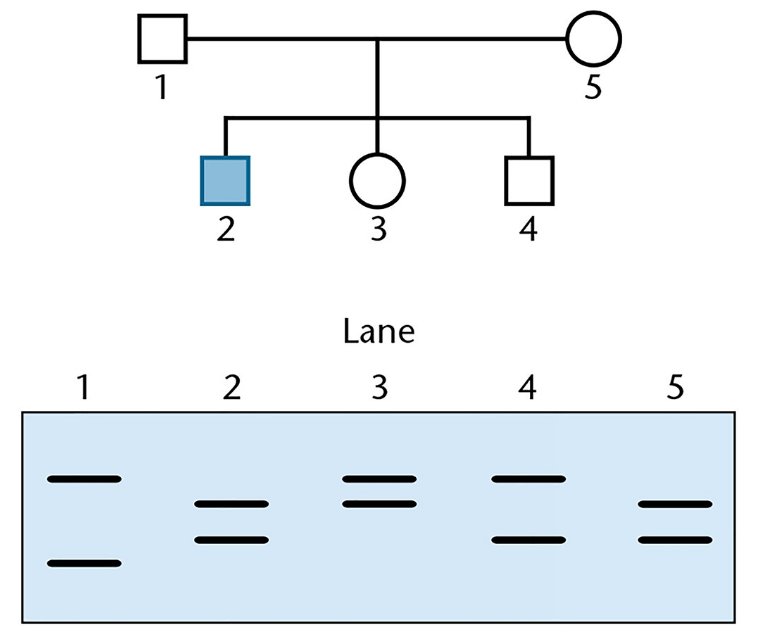
Prader–Willi syndrome (PWS) is a genetic disorder with a clinical profile of obesity, intellectual disability, and short stature. It can be caused in several ways. Most common is a deletion on the paternal copy of chromosome 15, but it can also be caused by an epigenetic imprinting disorder and uniparental disomy, an event in which the affected child receives two copies of the maternal chromosome 15. A child with PWS comes to your clinic for a diagnosis of the molecular basis for this condition. The gel below shows the results of testing with short tandem repeats (STRs) from the region of chromosome 15 associated with the disorder.
Based on your interpretation of the data, what is the cause of PWS in this case? Explain your reasoning.
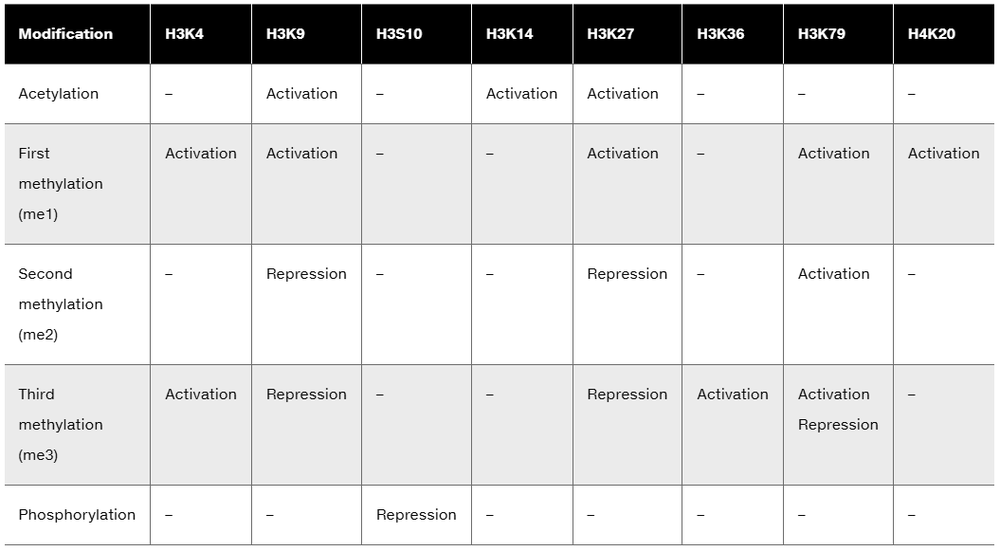
Problem 22a
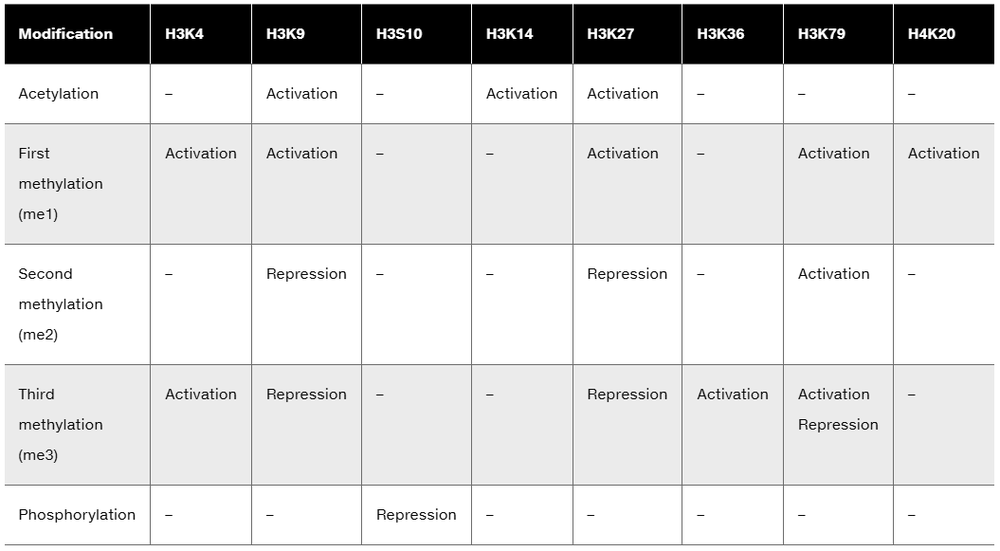
From the following table, draw up a list of histone H3 modifications associated with gene activation. Then draw up a list of H3 modifications associated with repression.
Are there any overlaps on the lists?
Problem 22b
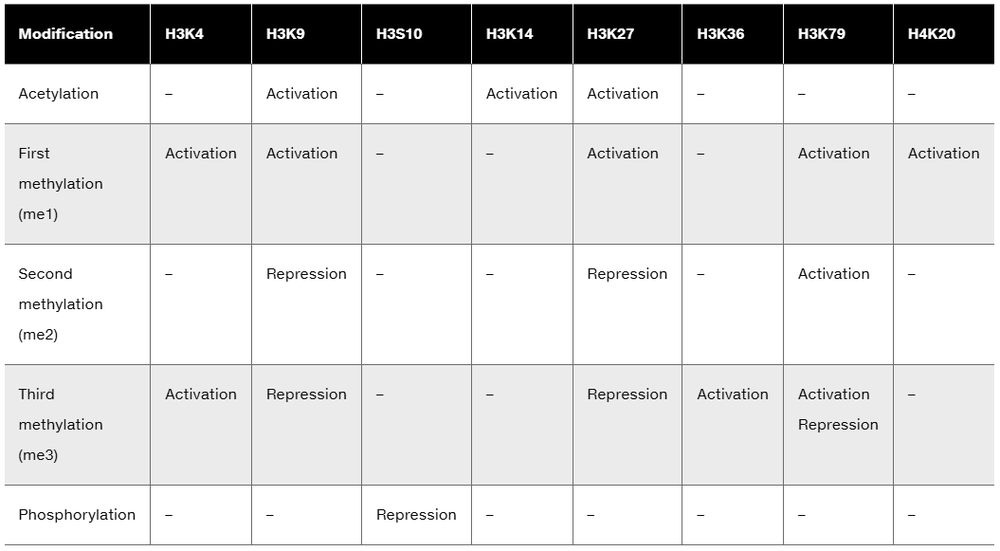
From the following table, draw up a list of histone H3 modifications associated with gene activation. Then draw up a list of H3 modifications associated with repression.
Are these overlaps explained by different modifications?
Problem 22c
From the following table, draw up a list of histone H3 modifications associated with gene activation. Then draw up a list of H3 modifications associated with repression.
If not, how can you reconcile these differences?
Problem 23a
Amino acids are classified as positively charged, negatively charged, or electrically neutral.
Which category includes lysine?