Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Ideal Gas Law
The Ideal Gas Law relates the pressure, volume, temperature, and number of moles of a gas through the equation PV = nRT. This law is fundamental in understanding how gases behave under varying conditions. In this scenario, with constant pressure, changes in temperature directly affect the volume of the gas.
Recommended video:
Ideal Gases and the Ideal Gas Law
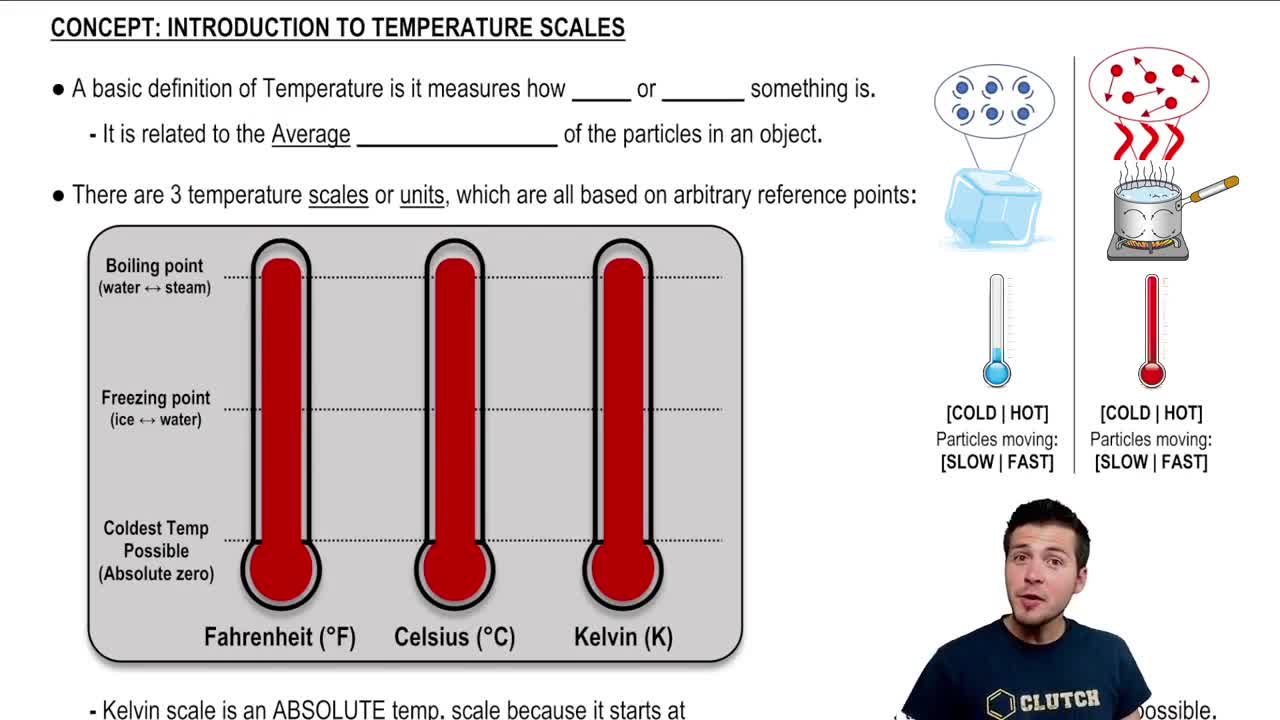
Temperature Scales
Temperature can be measured in different scales, with Celsius and Kelvin being the most common in physics. The Kelvin scale is an absolute temperature scale where 0 K represents absolute zero, the point at which molecular motion ceases. To convert Celsius to Kelvin, one adds 273.15, making it crucial to use Kelvin when applying gas laws.
Recommended video:
Introduction To Temperature Scales
Charles's Law
Charles's Law states that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature when pressure is held constant. This means that if the temperature increases, the volume must also increase, provided the pressure does not change. In this question, doubling the Kelvin temperature will lead to a corresponding increase in volume.
Recommended video: