Back
BackProblem 1
A chandelier hangs from a chain in the middle of a dining room. Identify the forces on the chandelier.
Problem 3
A baseball player is sliding into second base. Identify the forces on the baseball player.
Problem 5a
A jet plane is speeding down the runway during takeoff. Air resistance is not negligible. Identify the forces on the jet.
Problem 8
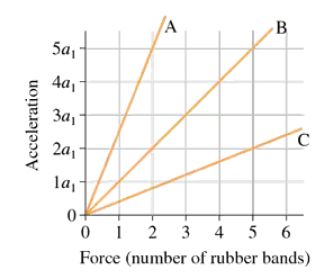
FIGURE EX5.8 shows an acceleration-versus-force graph for three objects pulled by rubber bands. The mass of object B is 0.20 kg. What are the masses of objects A and C? Explain your reasoning.
Problem 10
For an object starting from rest and accelerating with constant acceleration, distance traveled is proportional to the square of the time. If an object travels 2.0 furlongs in the first 2.0 s, how far will it travel in the first 4.0 s?
Problem 14
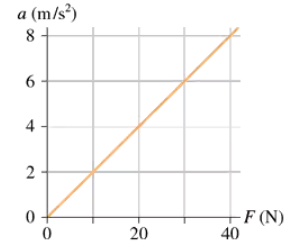
FIGURE EX5.14 shows an object's acceleration-versus-force graph. What is the object's mass?
Problem 16b
What is the acceleration, as a multiple of g, if this force is applied to a 110 kg bicyclist? This is the combined mass of the cyclist and the bike.
Problem 17
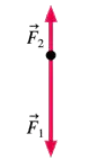
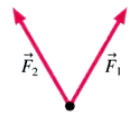
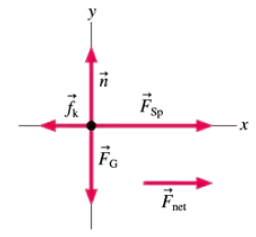
Newton's First Law Exercises 17, 18, and 19 show two of the three forces acting on an object in equilibrium. Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label the third force F3.
Problem 19c
Newton's First Law Exercises 17, 18, and 19 show two of the three forces acting on an object in equilibrium. Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label the third force F3.
Problem 24
Exercises 23, 24, 25, 26, and 27 describe a situation. For each, identify all forces acting on the object and draw a free-body diagram of the object. An ice hockey puck glides across frictionless ice.
Problem 25
Exercises 23, 24, 25, 26, and 27 describe a situation. For each, identify all forces acting on the object and draw a free-body diagram of the object. Your physics textbook is sliding across the table.
Problem 30
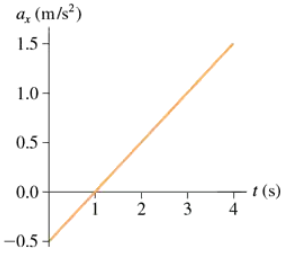
A single force with x-component Fₓ acts on a 500 g object as it moves along the x-axis. The object's acceleration graph aₓ versus t) is shown in FIGURE P5.30. Draw a graph of Fₓ versus t.
Problem 32
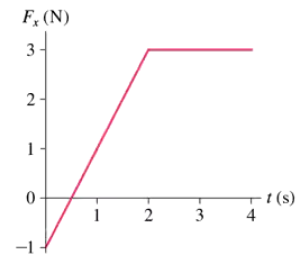
A single force with x-component Fₓ acts on a 2.0 kg object as it moves along the x-axis. A graph of Fₓ versus t is shown in FIGURE P5.32. Draw an acceleration graph aₓ versus t) for this object.
Problem 34a
A constant force is applied to an object, causing the object to accelerate at 10 m/s². What will the acceleration be if the force is halved?
Problem 34d
A constant force is applied to an object, causing the object to accelerate at 10 m/s². What will the acceleration be if The force is halved and the object's mass is doubled?
Problem 38a
Problems 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, and 40 show a free-body diagram. For each: Identify the direction of the acceleration vector a and show it as a vector next to your diagram. Or, if appropriate, write a = 0.
Problem 42
Problems 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, and 52 describe a situation. For each, draw a motion diagram, a force-identification diagram, and a free-body diagram. A Styrofoam ball has just been shot straight up. Air resistance is not negligible.
Problem 44
Problems 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, and 52 describe a situation. For each, draw a motion diagram, a force-identification diagram, and a free-body diagram. A rocket is being launched straight up. Air resistance is not negligible.
Problem 52
Problems 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, and 52 describe a situation. For each, draw a motion diagram, a force-identification diagram, and a free-body diagram. A model rocket is fired straight down from the top of a tower.
Problem 56a
A rubber ball bounces. We'd like to understand how the ball bounces. A rubber ball has been dropped and is bouncing off the floor. Draw a motion diagram of the ball during the brief time interval that it is in contact with the floor. Show 4 or 5 frames as the ball compresses, then another 4 or 5 frames as it expands. What is the direction of a during each of these parts of the motion?
Problem 56c
A rubber ball bounces. We'd like to understand how the ball bounces. Draw a free-body diagram of the ball during its contact with the ground. Is there a net force acting on the ball? If so, in which direction?
Problem 57b
If a car stops suddenly, you feel 'thrown forward.' We'd like to understand what happens to the passengers as a car stops. Imagine yourself sitting on a very slippery bench inside a car. This bench has no friction, no seat back, and there's nothing for you to hold onto. Draw your free-body diagram. Is there a net force on you? If so, in which direction?
Problem 57d
If a car stops suddenly, you feel 'thrown forward.' We'd like to understand what happens to the passengers as a car stops. Imagine yourself sitting on a very slippery bench inside a car. This bench has no friction, no seat back, and there's nothing for you to hold onto. Describe what happens to you as the car slows down.