Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Newton's Second Law of Motion
Newton's Second Law states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass. This relationship is expressed by the formula F = ma, where F is the net force, m is the mass, and a is the acceleration. Understanding this law is crucial for analyzing how changes in force and mass affect an object's acceleration.
Recommended video:
Intro to Forces & Newton's Second Law
Force and Mass Relationship
The relationship between force, mass, and acceleration is fundamental in physics. When the force applied to an object is altered, or when the mass of the object changes, the resulting acceleration will also change according to Newton's Second Law. Specifically, if the force is halved while the mass is doubled, the overall effect on acceleration must be calculated to determine the new acceleration.
Recommended video:
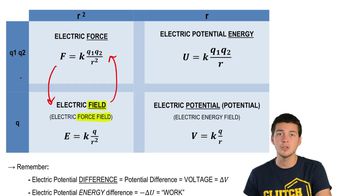
Relationships Between Force, Field, Energy, Potential
Acceleration Calculation
Acceleration is calculated by rearranging Newton's Second Law to a = F/m. In the scenario where the force is halved and the mass is doubled, the new acceleration can be determined by substituting the modified values into this equation. This calculation is essential for predicting how the object's motion will change under the new conditions.
Recommended video:
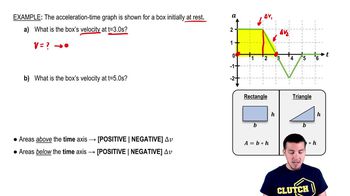
Calculating Change in Velocity from Acceleration-Time Graphs