Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Charles's Law
Charles's Law states that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature (in Kelvin) when pressure is held constant. This means that if the temperature increases, the volume will also increase, and vice versa. The relationship can be expressed mathematically as V₁/T₁ = V₂/T₂, where V is volume and T is temperature in Kelvin.
Recommended video:
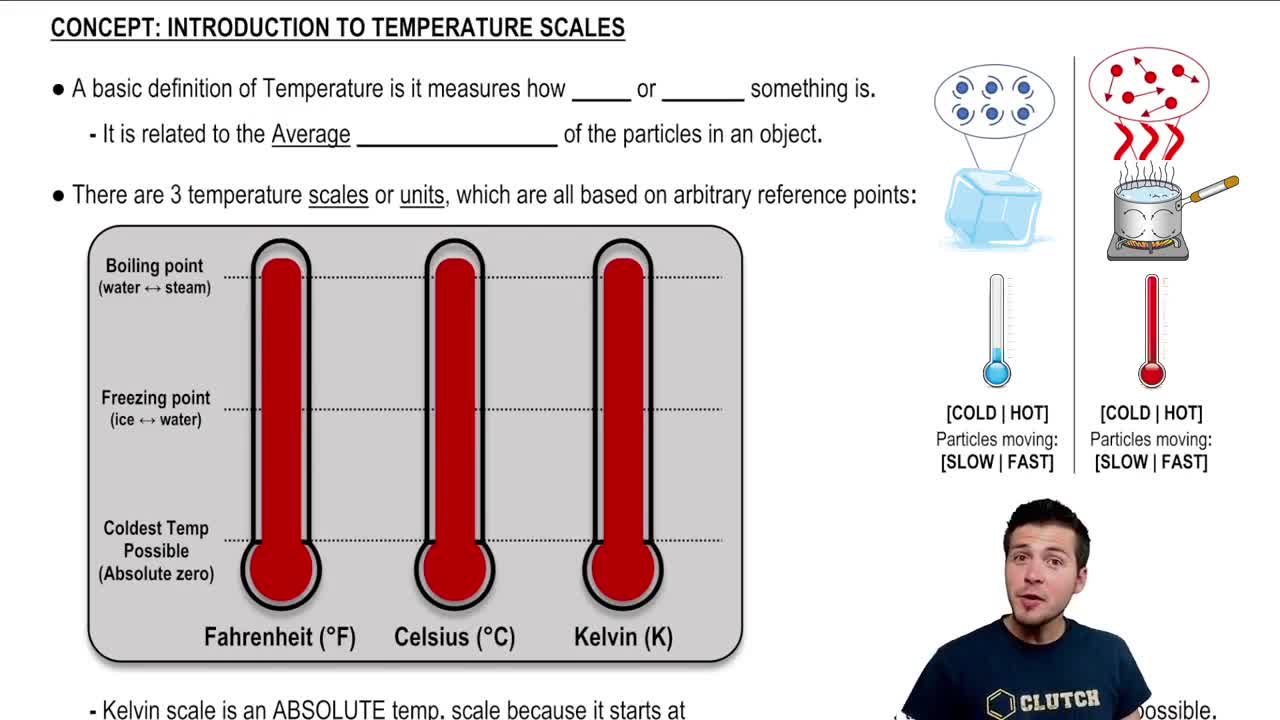
Absolute Temperature
Absolute temperature is measured on the Kelvin scale, where 0 K represents absolute zero, the point at which molecular motion ceases. To convert Celsius to Kelvin, you add 273.15. This conversion is crucial when applying gas laws, as they require temperatures to be in absolute terms to ensure accurate calculations.
Recommended video:
Introduction To Temperature Scales
Gas Behavior Under Constant Pressure
When a gas is subjected to constant pressure, any change in temperature will result in a corresponding change in volume, as described by Charles's Law. This principle is essential for understanding how gases expand or contract in response to temperature changes, which is particularly relevant in thermodynamic processes and applications.
Recommended video:
Phase Constant of a Wave Function
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance