An electron experiences a magnetic force of magnitude 4.60 x10-15 N when moving at an angle of 60.0° with respect to a magnetic field of magnitude 3.50 x 10-3 T. Find the speed of the electron.

A horizontal rectangular surface has dimensions 2.80 cm by 3.20 cm and is in a uniform magnetic field that is directed at an angle of 30.0° above the horizontal. What must the magnitude of the magnetic field be to produce a flux of 3.10 x 10-4 Wb through the surface?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Magnetic Flux
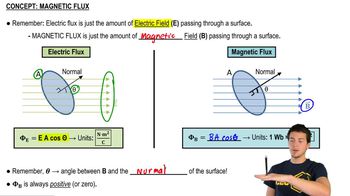
Area Calculation

Trigonometric Functions
A flat, square surface with side length is in the xy-plane at . Calculate the magnitude of the flux through this surface produced by a magnetic field .
A circular area with a radius of 6.50 cm lies in the xy-plane. What is the magnitude of the magnetic flux through this circle due to a uniform magnetic field B = 0.230 T at an angle of 53.1° from the +z-direction?
An open plastic soda bottle with an opening diameter of 2.5 cm is placed on a table. A uniform 1.75 T magnetic field directed upward and oriented 25° from vertical encompasses the bottle. What is the total magnetic flux through the plastic of the soda bottle?
A 150 g ball containing 4.00 x 108 excess electrons is dropped into a 125 m vertical shaft. At the bottom of the shaft, the ball suddenly enters a uniform horizontal magnetic field that has magnitude 0.250 T and direction from east to west. If air resistance is negligibly small, find the magnitude and direction of the force that this magnetic field exerts on the ball just as it enters the field.
Cyclotrons are widely used in nuclear medicine for producing short-lived radioactive isotopes. These cyclotrons typically accelerate H- (the hydride ion, which has one proton and two electrons) to an energy of 5 MeV to 20 MeV. This ion has a mass very close to that of a proton because the electron mass is negligible — about 1/2000 of the proton's mass. A typical magnetic field in such cyclotrons is 1.9 T. (a) What is the speed of a 5.0 MeV H-? (b) If the H- has energy 5.0 MeV and B = 1.9 T, what is the radius of this ion's circular orbit?
