Back
BackProblem 1
A 0.120-kg, 50.0-cm-long uniform bar has a small 0.055-kg mass glued to its left end and a small 0.110-kg mass glued to the other end. The two small masses can each be treated as point masses. You want to balance this system horizontally on a fulcrum placed just under its center of gravity. How far from the left end should the fulcrum be placed?
Problem 3
A uniform rod is 2.00 m long and has mass 1.80 kg. A 2.40 kg clamp is attached to the rod. How far should the center of gravity of the clamp be from the left-hand end of the rod in order for the center of gravity of the composite object to be 1.20 m from the left-hand end of the rod?
Problem 4a
A uniform 300-N trapdoor in a floor is hinged at one side. Find the net upward force needed to begin to open it and the total force exerted on the door by the hinges if the upward force is applied at the center.
Problem 4b
A uniform 300-N trapdoor in a floor is hinged at one side. Find the net upward force needed to begin to open it and the total force exerted on the door by the hinges if the upward force is applied at the center of the edge opposite the hinges.
Problem 6
Two people are carrying a uniform wooden board that is 3.00 m long and weighs 160 N. If one person applies an upward force equal to 60 N at one end, at what point does the other person lift? Begin with a free-body diagram of the board.
Problem 7a
Two people carry a heavy electric motor by placing it on a light board 2.00 m long. One person lifts at one end with a force of 400 N, and the other lifts the opposite end with a force of 600 N. What is the weight of the motor, and where along the board is its center of gravity located?
Problem 9
A 350-N, uniform, 1.50-m bar is suspended horizontally by two vertical cables at each end. Cable A can support a maximum tension of 500.0 N without breaking, and cable B can support up to 400.0 N. You want to place a small weight on this bar. (a) What is the heaviest weight you can put on without breaking either cable, and (b) where should you put this weight?
Problem 10a
A uniform ladder 5.0 m long rests against a frictionless, vertical wall with its lower end 3.0 m from the wall. The ladder weighs 160 N. The coefficient of static friction between the foot of the ladder and the ground is 0.40. A man weighing 740 N climbs slowly up the ladder. Start by drawing a free-body diagram of the ladder. What is the maximum friction force that the ground can exert on the ladder at its lower end?
Problem 11a
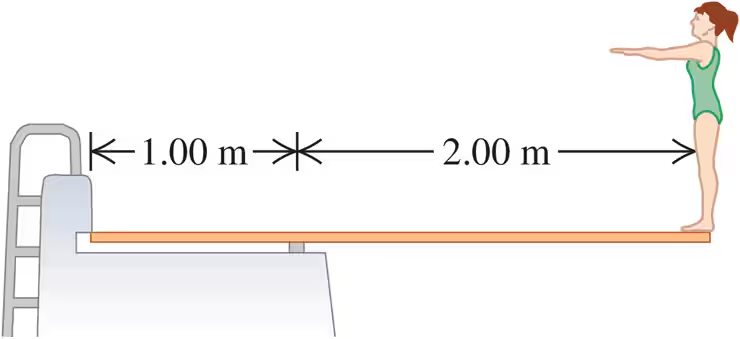
A diving board 3.00 m long is supported at a point 1.00 m from the end, and a diver weighing 500 N stands at the free end (Fig. E11.11). The diving board is of uniform cross section and weighs 280 N. Find the force at the support point.
Problem 13a
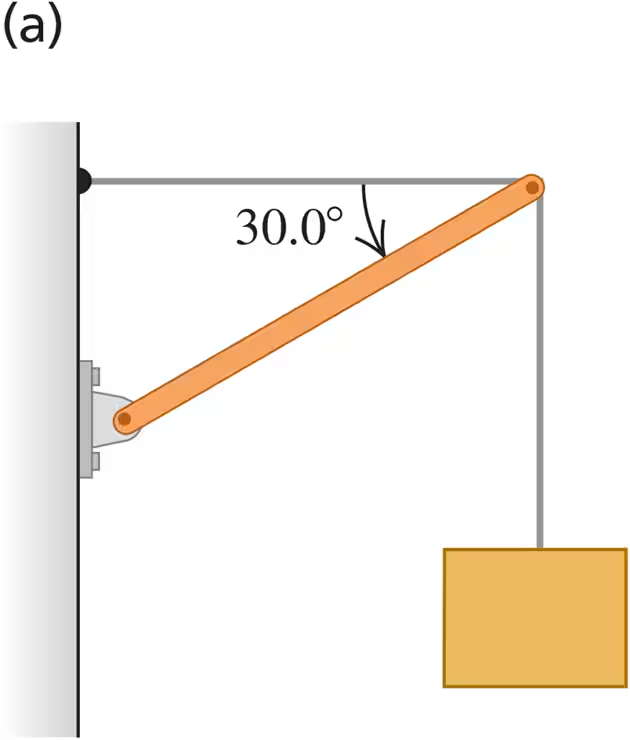
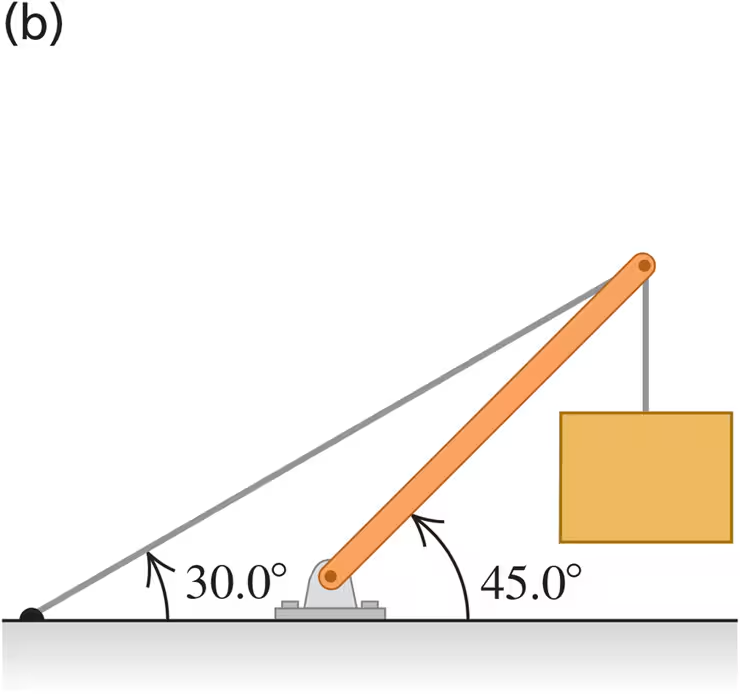
Find the tension T in each cable and the magnitude and direction of the force exerted on the strut by the pivot in each of the arrangements in Fig. E11.13. In each case let w be the weight of the suspended crate full of priceless art objects. The strut is uniform and also has weight w. Start each case with a free-body diagram of the strut.
Problem 13b
Find the tension T in each cable and the magnitude and direction of the force exerted on the strut by the pivot in each of the arrangements in Fig. E11.13. In each case let w be the weight of the suspended crate full of priceless art objects. The strut is uniform and also has weight w. Start each case with a free-body diagram of the strut.
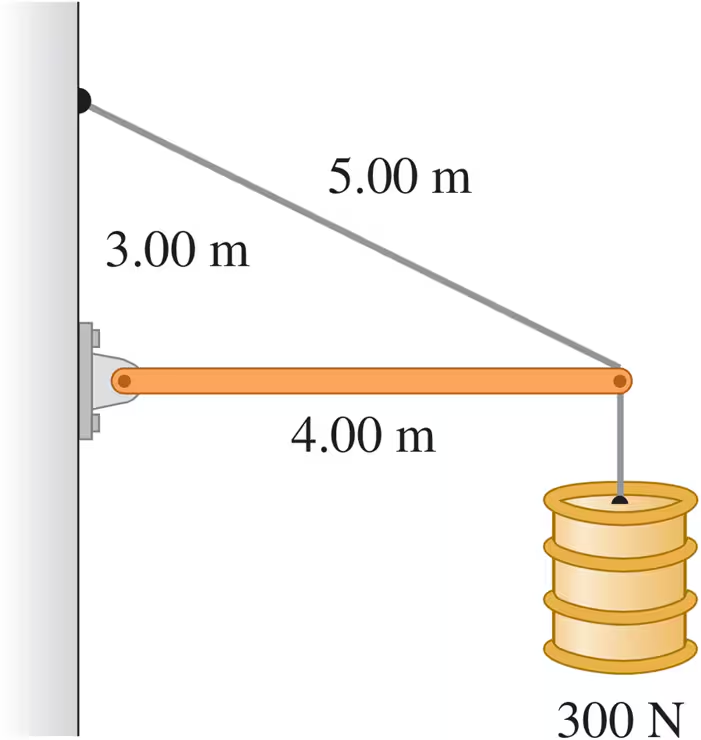
Problem 14a
The horizontal beam in Fig. E11.14 weighs 190 N, and its center of gravity is at its center. Find the tension in the cable.
Problem 14b
The horizontal beam in Fig. E11.14 weighs 190 N, and its center of gravity is at its center. Find the horizontal and vertical components of the force exerted on the beam at the wall.
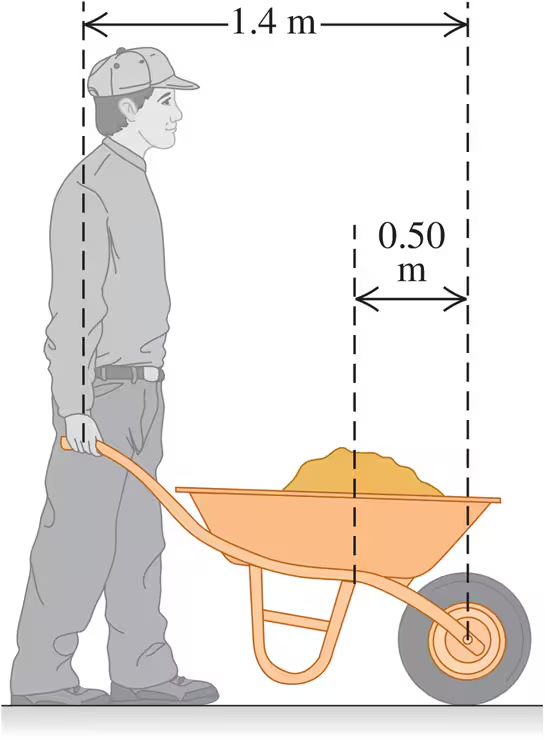
Problem 16a
Suppose that you can lift no more than 650 N (around 150 lb) unaided.
How much can you lift using a 1.4 m-long wheelbarrow that weighs 80.0 N and whose center of gravity is 0.50 m from the center of the wheel (Fig. E11.16)? The center of gravity of the load carried in the wheelbarrow is also 0.50 m from the center of the wheel.

Problem 16b
Suppose that you can lift no more than 650 N (around 150 lb) unaided.
(a) How much can you lift using a 1.4-m-long wheelbarrow that weighs 80.0 N and whose center of gravity is 0.50 m from the center of the wheel (Fig. E11.16)? The cen-ter of gravity of the load car-ried in the wheelbarrow is also 0.50 m from the center of the wheel. (b) Where does the force come from to enable you to lift more than 650 N using the wheelbarrow?
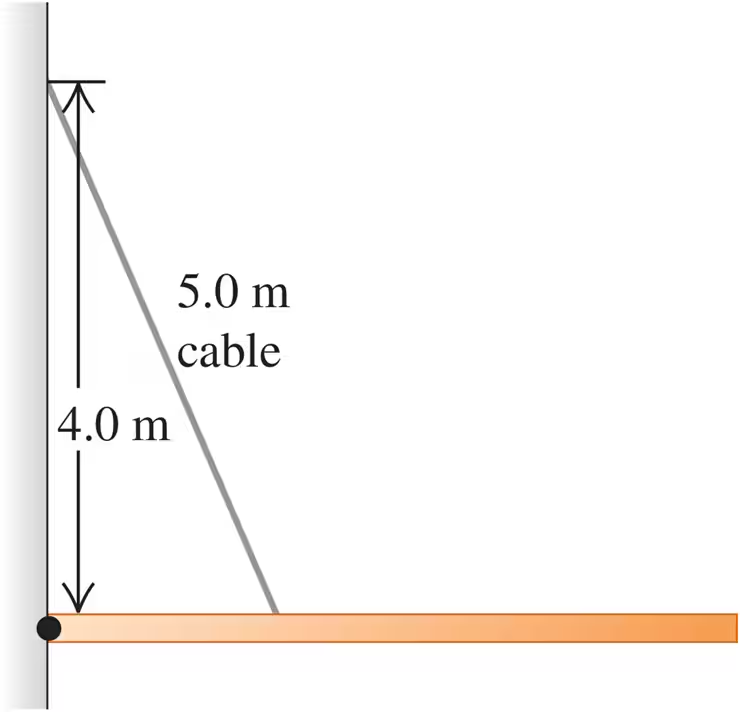
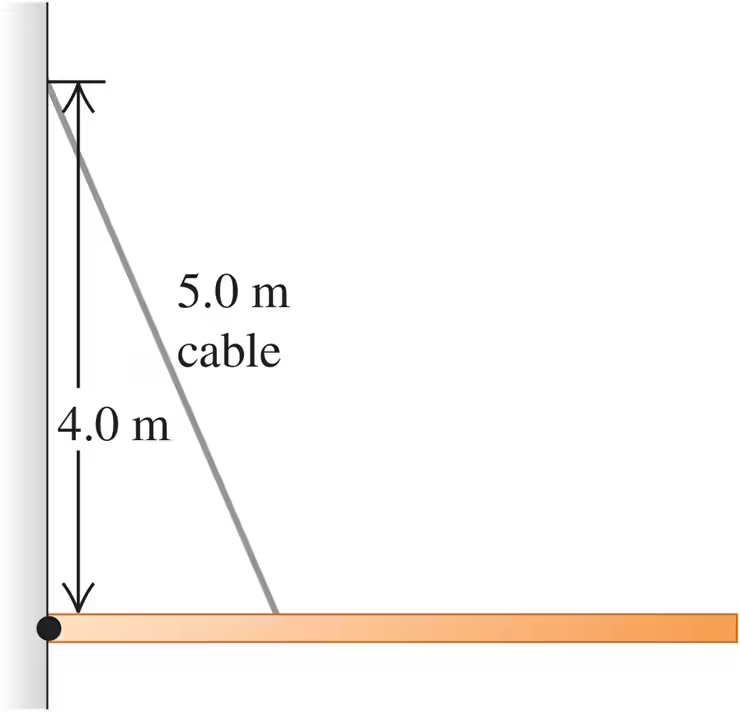
Problem 17b
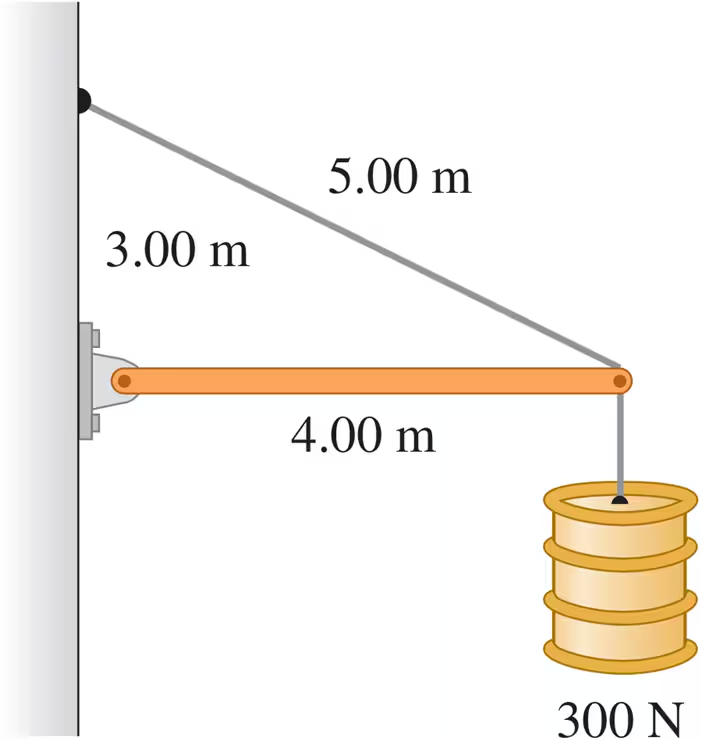
A 9.00-m-long uniform beam is hinged to a vertical wall and held horizontally by a 5.00-m-long cable attached to the wall 4.00 m above the hinge (Fig. E11.17). The metal of this cable has a test strength of 1.00 kN, which means that it will break if the tension in it exceeds that amount. What is the heaviest beam that the cable can support in this configuration?
Problem 17c
A 9.00 m-long uniform beam is hinged to a vertical wall and held horizontally by a 5.00 m-long cable attached to the wall 4.00 m above the hinge (Fig. E11.17). The metal of this cable has a test strength of 1.00 kN, which means that it will break if the tension in it exceeds that amount. Find the horizontal and vertical components of the force the hinge exerts on the beam. Is the vertical component upward or downward?
Problem 18a
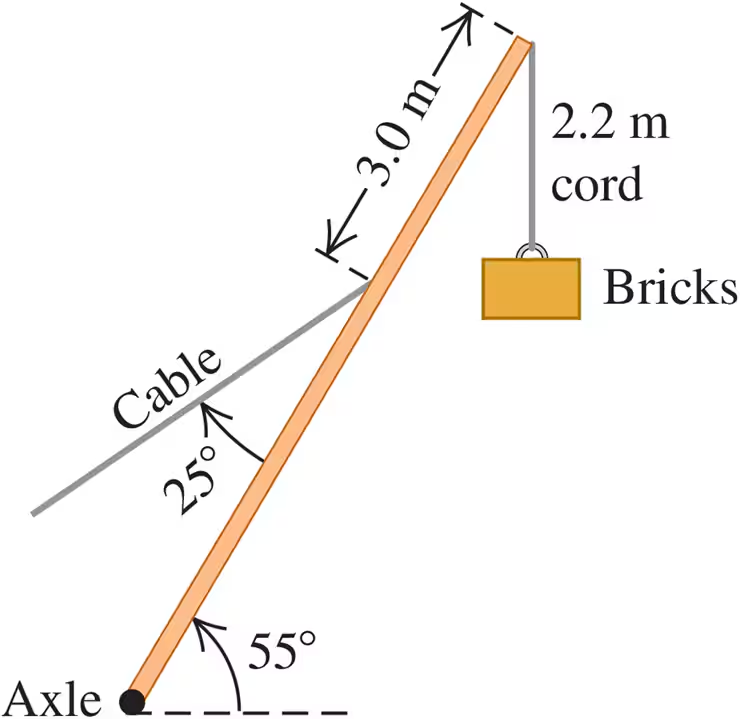
A 15,000-N crane pivots around a friction-free axle at its base and is supported by a cable making a 25° angle with the crane (Fig. E11.18). The crane is 16 m long and is not uniform, its center of gravity being 7.0 m from the axle as measured along the crane. The cable is attached 3.0 m from the upper end of the crane. When the crane is raised to 55° above the horizontal holding an 11,000-N pallet of bricks by a 2.2-m, very light cord, find the tension in the cable. Start with a free-body diagram of the crane.
Problem 20
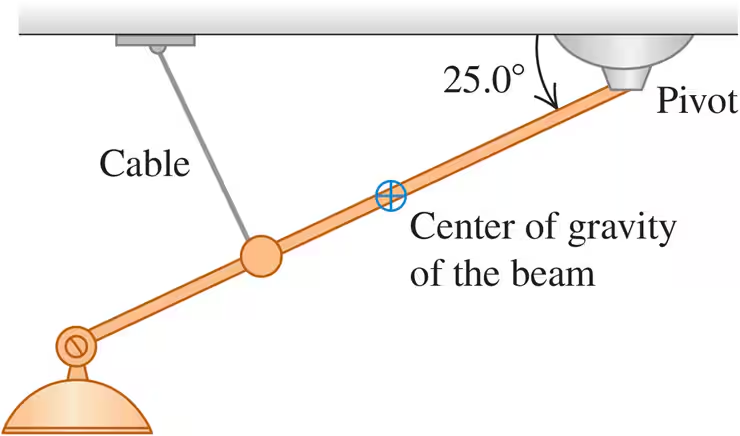
A nonuniform beam 4.50 m long and weighing 1.40 kN makes an angle of 25.0° below the horizontal. It is held in position by a frictionless pivot at its upper right end and by a cable 3.00 m farther down the beam and perpendicular to it (Fig. E11.20). The center of gravity of the beam is 2.00 m down the beam from the pivot. Lighting equipment exerts a 5.00-kN downward force on the lower left end of the beam. Find the tension T in the cable and the horizontal and vertical components of the force exerted on the beam by the pivot. Start by sketching a free-body diagram of the beam.
Problem 25
A circular steel wire 2.00 m long must stretch no more than 0.25 cm when a tensile force of 700 N is applied to each end of the wire. What minimum diameter is required for the wire?
Problem 26
Two circular rods, one steel and the other copper, are joined end to end. Each rod is 0.750 m long and 1.50 cm in diameter. The combination is subjected to a tensile force with magnitude 4000 N. For each rod, what are (a) the strain and (b) the elongation?
Problem 28
A nylon rope used by mountaineers elongates 1.10 m under the weight of a 65.0 kg climber. If the rope is 45.0 m in length and 7.0 mm in diameter, what is Young's modulus for nylon?
Problem 32c
A solid gold bar is pulled up from the hold of the sunken RMS Titanic. The bulk modulus of lead is one-fourth that of gold. Find the ratio of the volume change of a solid lead bar to that of a gold bar of equal volume for the same pressure change.
Problem 33
A specimen of oil having an initial volume of 600 cm3 is subjected to a pressure increase of 3.6×106 Pa, and the volume is found to decrease by 0.45 cm3. What is the bulk modulus of the material and the compressibility?
Problem 34a
In the Challenger Deep of the Marianas Trench, the depth of seawater is 10.9 km and the pressure is 1.16×108 Pa (about 1.15×103 atm). If a cubic meter of water is taken from the surface to this depth, what is the change in its volume? (Normal atmospheric pressure is about 1.0×105 Pa. Assume that k for seawater is the same as the freshwater value given in Table 11.2.)
Problem 36
A square steel plate is 10.0 cm on a side and 0.500 cm thick. (a) Find the shear strain that results if a force of magnitude 9.0×105 N is applied to each of the four sides, parallel to the side. (b) Find the displacement x (in centimeters).
Problem 38
A brass wire is to withstand a tensile force of 350 N without breaking. What minimum diameter must the wire have?