Back
BackProblem 4b
A concave mirror has a radius of curvature of 34.0 cm. If the mirror is immersed in water (refractive index 1.33), what is its focal length?
Problem 5b
An object 0.600 cm tall is placed 16.5 cm to the left of the vertex of a concave spherical mirror having a radius of curvature of 22.0 cm. Determine the position, size, orientation, and nature (real or virtual) of the image.
Problem 8
An object is 18.0 cm from the center of a spherical silvered-glass Christmas tree ornament 6.00 cm in diameter. What are the position and magnification of its ?
Problem 10a
You hold a spherical salad bowl 60 cm in front of your face with the bottom of the bowl facing you. The bowl is made of polished metal with a 35-cm radius of curvature. Where is the of your 5.0-cm tall nose located?
Problem 11b
A spherical, concave shaving mirror has a radius of curvature of 32.0 cm. Where is the image? Is the image real or virtual?
Problem 13b
Dental Mirror. A dentist uses a curved mirror to view teeth on the upper side of the mouth. Suppose she wants an erect with a magnification of 2.00 when the mirror is 1.25 cm from a tooth. (Treat this problem as though the object and lie along a straight line.) What must be the focal length and radius of curvature of this mirror?
Problem 15a
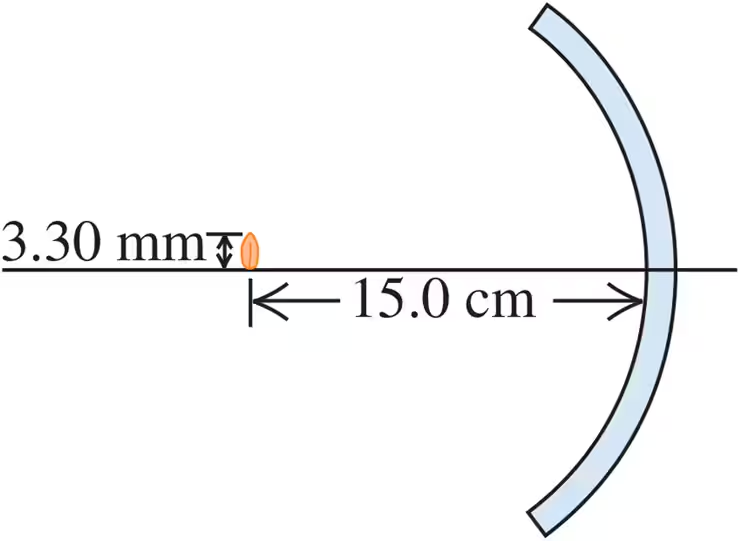
The thin glass shell shown in Fig. E34.15 has a spherical shape with a radius of curvature of 12.0 cm, and both of its surfaces can act as mirrors. A seed 3.30 mm high is placed 15.0 cm from the center of the mirror along the optic axis, as shown in the figure. Calculate the location and height of the of this seed.
Problem 20a
A person is lying on a diving board 3.00 m above the surface of the water in a swimming pool. She looks at a penny that is on the bottom of the pool directly below her. To her, the penny appears to be a distance of 7.00 m from her. What is the depth of the water at this point?
Problem 21a
A Spherical Fish Bowl. A small tropical fish is at the center of a water-filled, spherical fish bowl 28.0 cm in diameter. Find the apparent position and magnification of the fish to an observer outside the bowl. The effect of the thin walls of the bowl may be ignored.
Problem 23
The glass rod of Exercise 34.22 is immersed in oil (n = 1.45). An object placed to the left of the rod on the rod's axis is to be d 1.20 m inside the rod. How far from the left end of the rod must the object be located to form the image?
Problem 24
The left end of a long glass rod 8.00 cm in diameter, with an index of refraction of 1.60, is ground and polished to a convex hemispherical surface with a radius of 4.00 cm. An object in the form of an arrow 1.50 mm tall, at right angles to the axis of the rod, is located on the axis 24.0 cm to the left of the vertex of the convex surface. Find the position and height of the of the arrow formed by paraxial rays incident on the convex surface. Is the erect or inverted?
Problem 28a
A lens forms an of an object. The object is 16.0 cm from the lens. The is 12.0 cm from the lens on the same side as the object. What is the focal length of the lens? Is the lens converging or diverging?
Problem 30
A converging lens with a focal length of 70.0 cm forms an image of a 3.20 cm tall real object that is to the left of the lens. The image is 4.50 cm tall and inverted. Where are the object and image located in relation to the lens? Is the image real or virtual?
Problem 34a
A converging lens with a focal length of 9.00 cm forms an image of a 4.00 mm tall real object that is to the left of the lens. The image is 1.30 cm tall and erect. Where are the object and image located? Is the image real or virtual?
Problem 36
A lensmaker wants to make a magnifying glass from glass that has an index of refraction n = 1.55 and a focal length of 20.0 cm. If the two surfaces of the lens are to have equal radii, what should that radius be?
Problem 37b
For each thin lens shown in Fig. E34.37, calculate the location of the image of an object that is 18.0 cm to the left of the lens. The lens material has a refractive index of 1.50, and the radii of curvature shown are only the magnitudes.
Problem 40b
An object is 16.0 cm to the left of a lens. The lens forms an image 36.0 cm to the right of the lens. If the object is 8.00 mm tall, how tall is the image? Is it erect or inverted?
Problem 40c
An object is 16.0 cm to the left of a lens. The lens forms an image 36.0 cm to the right of the lens. Draw a principal-ray diagram.
Problem 41a
A 1.20 cm tall object is 50.0 cm to the left of a converging lens of focal length 40.0 cm. A second converging lens, this one having a focal length of 60.0 cm, is located 300.0 cm to the right of the first lens along the same optic axis. Find the location and height of the image (call it I1) formed by the lens with a focal length of 40.0 cm.
Problem 42a
Repeat Exercise 34.41 using the same lenses except for the following changes: The second lens is a diverging lens having a focal length of magnitude 60.0 cm.
Problem 44a
BIO The Lens of the Eye. The crystalline lens of the human eye is a double-convex lens made of material having an index of refraction of 1.44 (although this varies). Its focal length in air is about 8.0 mm, which also varies. We shall assume that the radii of curvature of its two surfaces have the same magnitude. Find the radii of curvature of this lens.
Problem 46b
You wish to project the image of a slide on a screen 9.00 m from the lens of a slide projector. If the dimensions of the picture on a 35 mm color slide are 24 mm ✖ 36 mm, what is the minimum size of the projector screen required to accommodate the image?
Problem 48ac
Zoom Lens. Consider the simple model of the zoom lens shown in Fig. 34.43a. The converging lens has focal length f1 = 12 cm, and the diverging lens has focal length f2 = -12 cm. The lenses are separated by 4 cm as shown in Fig. 34.43a. (a) For a distant object, where is the of the converging lens? (c) Where is the final image? Compare your answer to Fig. 34.43a.
Problem 49a
A camera lens has a focal length of 180.0 mm and an aperture diameter of 16.36 mm. What is the ƒ-number of the lens?
Problem 51a
Where is the near point of an eye for which a contact lens with a power of +2.75 diopters is prescribed?
Problem 52a
Contact lenses are placed right on the eyeball, so the distance from the eye to an object (or image) is the same as the distance from the lens to that object (or image). A certain person can see distant objects well, but his near point is 45.0 cm from his eyes instead of the usual 25.0 cm. Is this person nearsighted or farsighted?
Problem 53
BIO Ordinary Glasses. Ordinary glasses are worn in front of the eye and usually 2.0 cm in front of the eyeball. Suppose that the person in Exercise 34.52 prefers ordinary glasses to contact lenses. What focal length lenses are needed to correct his vision, and what is their power in diopters?
Problem 54a
BIO A person can see clearly up close but cannot focus on objects beyond 75.0 cm. She opts for contact lenses to correct her vision. Is she nearsighted or farsighted?
Problem 54c
BIO A person can see clearly up close but cannot focus on objects beyond 75.0 cm. She opts for contact lenses to correct her vision. What focal length contact lens is needed, and what is its power in diopters?
Problem 56a
A thin lens with a focal length of 6.00 cm is used as a simple magnifier. What angular magnification is obtainable with the lens if the object is at the focal point?