Back
BackProblem 4
A particle with mass and a charge of has, at a given instant, a velocity . What are the magnitude and direction of the particle's acceleration produced by a uniform magnetic field ?
Problem 5
An electron experiences a magnetic force of magnitude 4.60 x10-15 N when moving at an angle of 60.0° with respect to a magnetic field of magnitude 3.50 x 10-3 T. Find the speed of the electron.
Problem 10
A flat, square surface with side length is in the xy-plane at . Calculate the magnitude of the flux through this surface produced by a magnetic field .
Problem 11b
A circular area with a radius of 6.50 cm lies in the xy-plane. What is the magnitude of the magnetic flux through this circle due to a uniform magnetic field B = 0.230 T at an angle of 53.1° from the +z-direction?
Problem 12
A horizontal rectangular surface has dimensions 2.80 cm by 3.20 cm and is in a uniform magnetic field that is directed at an angle of 30.0° above the horizontal. What must the magnitude of the magnetic field be to produce a flux of 3.10 x 10-4 Wb through the surface?
Problem 13
An open plastic soda bottle with an opening diameter of 2.5 cm is placed on a table. A uniform 1.75 T magnetic field directed upward and oriented 25° from vertical encompasses the bottle. What is the total magnetic flux through the plastic of the soda bottle?
Problem 17
A 150 g ball containing 4.00 x 108 excess electrons is dropped into a 125 m vertical shaft. At the bottom of the shaft, the ball suddenly enters a uniform horizontal magnetic field that has magnitude 0.250 T and direction from east to west. If air resistance is negligibly small, find the magnitude and direction of the force that this magnetic field exerts on the ball just as it enters the field.
Problem 20
Cyclotrons are widely used in nuclear medicine for producing short-lived radioactive isotopes. These cyclotrons typically accelerate H- (the hydride ion, which has one proton and two electrons) to an energy of 5 MeV to 20 MeV. This ion has a mass very close to that of a proton because the electron mass is negligible — about 1/2000 of the proton's mass. A typical magnetic field in such cyclotrons is 1.9 T. (a) What is the speed of a 5.0 MeV H-? (b) If the H- has energy 5.0 MeV and B = 1.9 T, what is the radius of this ion's circular orbit?
Problem 21
A deuteron (the nucleus of an isotope of hydrogen) has a mass of 3.34 x 10-27 kg and a charge of +e. The deuteron travels in a circular path with a radius of 6.96 mm in a magnetic field with magnitude 2.50 T. (a) Find the speed of the deuteron. (b) Find the time required for it to make half a revolution. (c) Through what potential difference would the deuteron have to be accelerated to acquire this speed?
Problem 22
In a cyclotron, the orbital radius of protons with energy 300 keV is 16.0 cm. You are redesigning the cyclotron to be used instead for alpha particles with energy 300 keV. An alpha particle has charge q = +2e and mass m = 6.64 x 10-27 kg. If the magnetic field isn't changed, what will be the orbital radius of the alpha particles?
Problem 24
A beam of protons traveling at 1.20 km/s enters a uniform magnetic field, traveling perpendicular to the field. The beam exits the magnetic field, leaving the field in a direction perpendicular to its original direction (Fig. E27.24) . The beam travels a distance of 1.18 cm while in the field. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field?
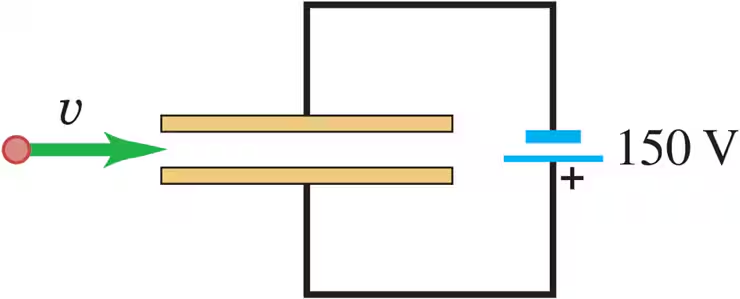
Problem 29
A 150 V battery is connected across two parallel metal plates of area 28.5 cm2 and separation 8.20 mm. A beam of alpha particles (charge +2e, mass 6.64 x 10-27 kg) is accelerated from rest through a potential difference of 1.75 kV and enters the region between the plates perpendicular to the electric field, as shown in Fig. E27.29. What magnitude and direction of magnetic field are needed so that the alpha particles emerge undeflected from between the plates?
Problem 31
Singly ionized (one electron removed) atoms are accelerated and then passed through a velocity selector consisting of perpendicular electric and magnetic fields. The electric field is 155 V/m and the magnetic field is 0.0315 T. The ions next enter a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.0175 T that is oriented perpendicular to their velocity. (a) How fast are the ions moving when they emerge from the velocity selector? (b) If the radius of the path of the ions in the second magnetic field is 17.5 cm, what is their mass?
Problem 34
A straight, 2.5 m wire carries a typical household current of 1.5 A (in one direction) at a location where the earth's magnetic field is 0.55 gauss from south to north. Find the magnitude and direction of the force that our planet's magnetic field exerts on this wire if it is oriented so that the current in it is running (a) from west to east, (b) vertically upward, (c) from north to south. (d) Is the magnetic force ever large enough to cause significant effects under normal household conditions?
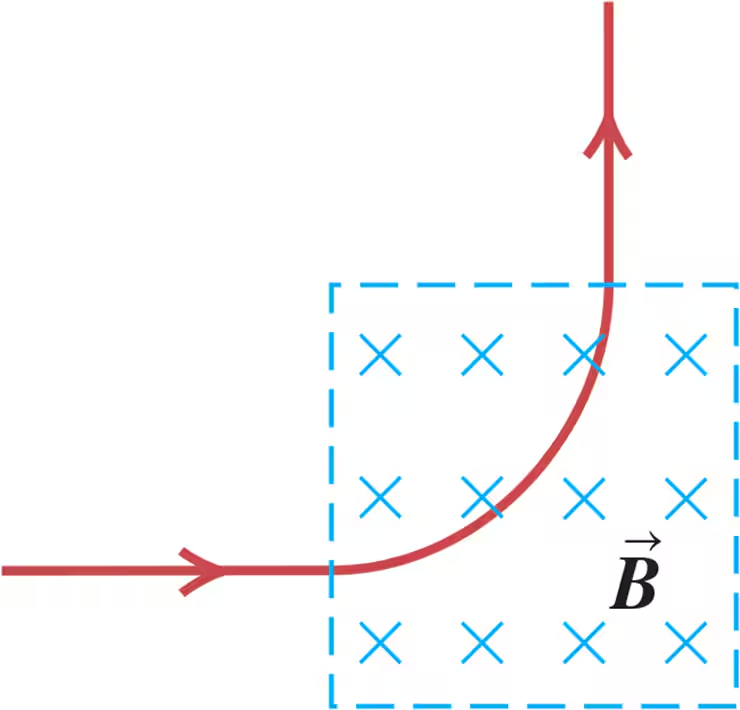
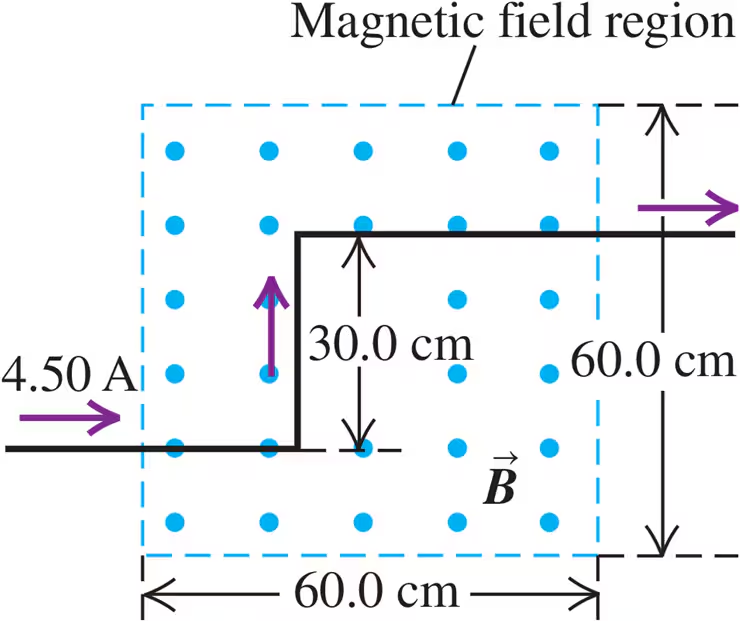
Problem 35
A long wire carrying 4.50 A of current makes two 90° bends, as shown in Fig. E27.35. The bent part of the wire passes through a uniform 0.240 T magnetic field directed as shown in the figure and confined to a limited region of space. Find the magnitude and direction of the force that the magnetic field exerts on the wire.
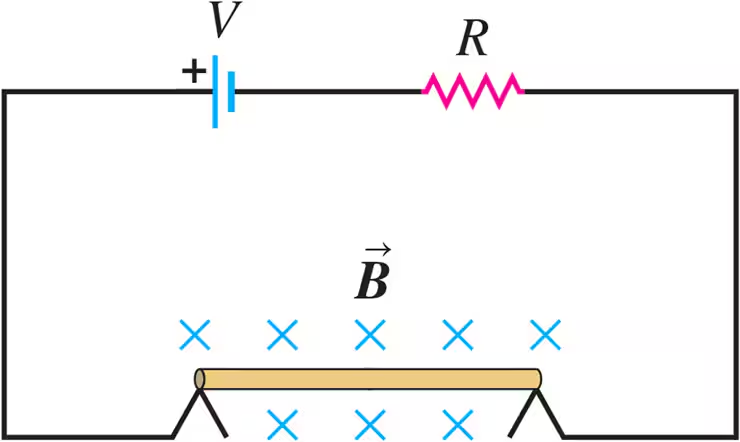
Problem 37
A thin, 50.0 cm long metal bar with mass 750 g rests on, but is not attached to, two metallic supports in a uniform 0.450 T magnetic field, as shown in Fig. E27.37. A battery and a 25.0 Ω resistor in series are connected to the supports. (a) What is the highest voltage the battery can have without breaking the circuit at the supports? (b) The battery voltage has the maximum value calculated in part (a). If the resistor suddenly gets partially short-circuited, decreasing its resistance to 2.00 Ω, find the initial acceleration of the bar.
Problem 38a
A straight, vertical wire carries a current of 2.60 A downward in a region between the poles of a large superconducting electromagnet, where the magnetic field has magnitude B = 0.588 T and is horizontal. What are the magnitude and direction of the magnetic force on a 1.00 cm section of the wire that is in this uniform magnetic field, if the magnetic field direction is (a) east?
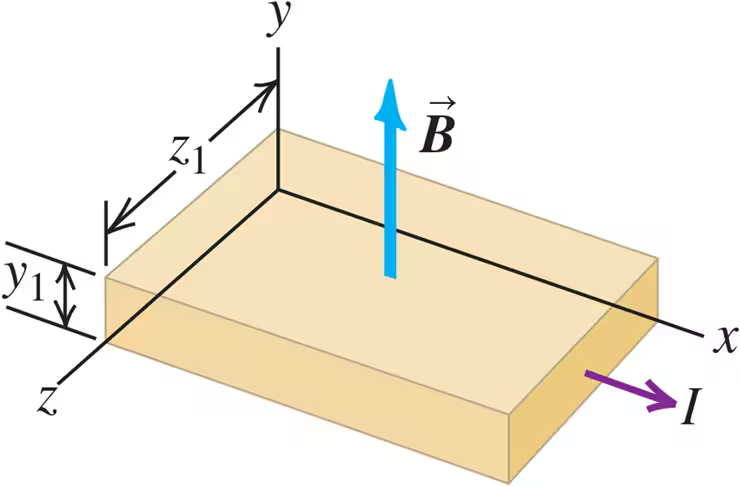
Problem 49
Figure E27.49 shows a portion of a silver ribbon with z1 = 11.8 mm and y1 = 0.23 mm, carrying a current of 120 A in the +x-direction. The ribbon lies in a uniform magnetic field, in the y-direction, with magnitude 0.95 T. Apply the simplified model of the Hall effect presented in Section 27.9. If there are 5.85 x 1028 free electrons per cubic meter, find (a) the magnitude of the drift velocity of the electrons in the x-direction; (b) the magnitude and direction of the electric field in the z-direction due to the Hall effect; (c) the Hall emf.