Back
BackProblem 7a
The current in a wire varies with time according to the relationship . How many coulombs of charge pass a cross section of the wire in the time interval between and ?
Problem 7b
The current in a wire varies with time according to the relationship . What constant current would transport the same charge in the same time interval?
Problem 15c
A cylindrical tungsten filament cm long with a diameter of mm is to be used in a machine for which the temperature will range from room temperature (°C) up to °C. It will carry a current of A at all temperatures. What will be the maximum potential drop over the full length of the filament?
Problem 17
In household wiring, copper wire mm in diameter is often used. Find the resistance of a -m length of this wire.
Problem 18
A ductile metal wire has resistance . What will be the resistance of this wire in terms of if it is stretched to three times its original length, assuming that the density and resistivity of the material do not change when the wire is stretched? (Hint: The amount of metal does not change, so stretching out the wire will affect its cross-sectional area.)
Problem 22
A hollow aluminum cylinder is m long and has an inner radius of cm and an outer radius of cm. Treat each surface (inner, outer, and the two end faces) as an equipotential surface. At room temperature, what will an ohmmeter read if it is connected between (a) the opposite faces and (b) the inner and outer surfaces?
Problem 23b
What is the resistance of a carbon rod at °C if its resistance is at °C?
Problem 25b
A copper transmission cable km long and cm in diameter carries a current of A. How much electrical energy is dissipated as thermal energy every hour?
Problem 28a
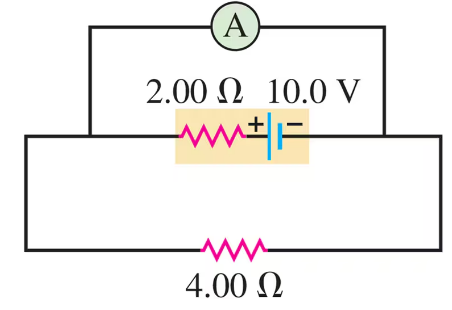
An idealized ammeter is connected to a battery as shown in Fig. E. Find the reading of the ammeter.
Problem 28b
An idealized ammeter is connected to a battery as shown in Fig. E. Find the current through the - resistor.
Problem 28c
An idealized ammeter is connected to a battery as shown in Fig. E. Find the terminal voltage of the battery.
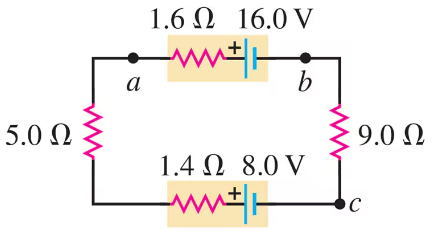
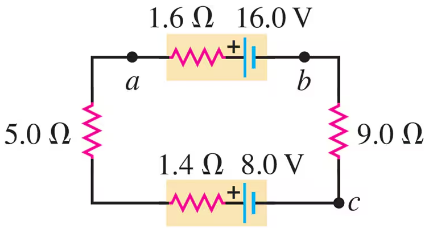
Problem 30
The circuit shown in Fig. E contains two batteries, each with an emf and an internal resistance, and two resistors. Find the potential difference of point with respect to point .
Problem 33a
The circuit shown in Fig. E contains two batteries, each with an emf and an internal resistance, and two resistors. Find the current in the circuit (magnitude and direction).
Problem 33b
The circuit shown in Fig. E contains two batteries, each with an emf and an internal resistance, and two resistors. Find the terminal voltage of the -V battery.
Problem 34a
When a resistor with resistance is connected to a -V flashlight battery, the resistor consumes W of electrical power. (Throughout, assume that each battery has negligible internal resistance.) What power does the resistor consume if it is connected to a -V car battery? Assume that remains constant when the power consumption changes.
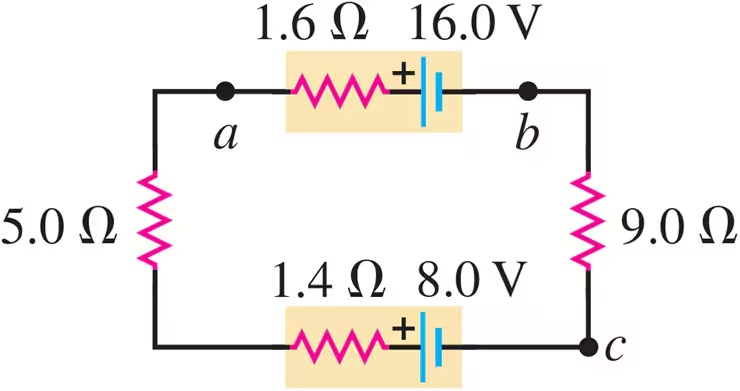
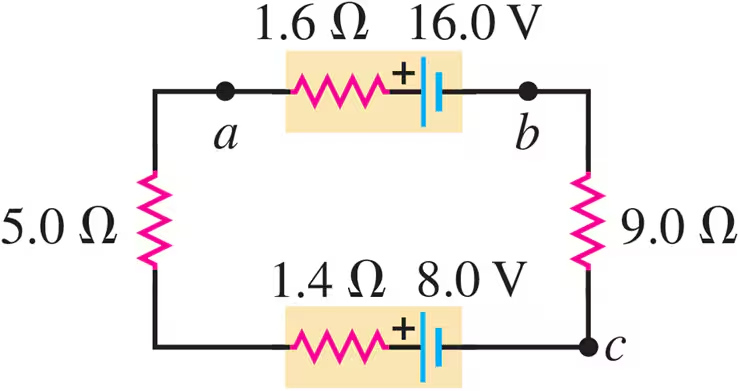
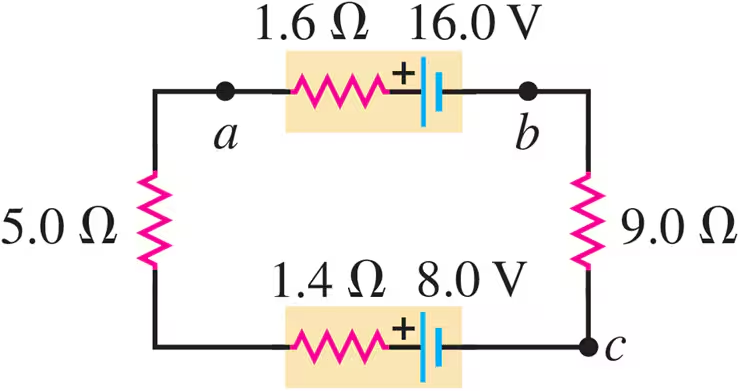
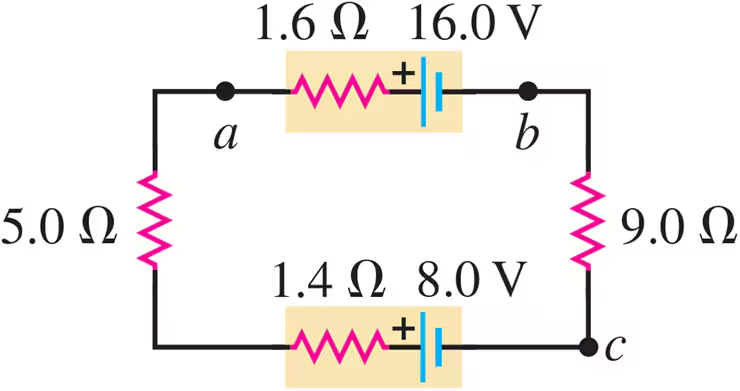
Problem 39a
Consider the circuit of Fig. E25.30. What is the total rate at which electrical energy is dissipated in the 5.0 Ω and 9.0 Ω resistors?
Problem 39b
Consider the circuit of Fig. E25.30. What is the power output of the 16.0 V battery?
Problem 39c
Consider the circuit of Fig. E25.30. At what rate is electrical energy being converted to other forms in the 8.0 V battery?
Problem 39d
Consider the circuit of Fig. E25.30 Show that the power output of the 16.0 V battery equals the overall rate of consumption of electrical energy in the rest of the circuit.
Problem 40
Electric eels generate electric pulses along their skin that can be used to stun an enemy when they come into contact with it. Tests have shown that these pulses can be up to 500 V and produce currents of 80 mA (or even larger). A typical pulse lasts for 10 ms. What power and how much energy are delivered to the unfortunate enemy with a single pulse, assuming a steady current?
Problem 41b
A heart defibrillator is used to enable the heart to start beating if it has stopped. This is done by passing a large current of 12 A through the body at 25 V for a very short time, usually about 3.0 ms. How much energy is transferred?
Problem 42
The battery for a certain cell phone is rated at 3.70 V. According to the manufacturer, it can produce 3.15 × 104 J of electrical energy, enough for 5.25 h of operation, before needing to be recharged. Find the average current that this cell phone draws when turned on.
Problem 46a
A typical small flashlight contains two batteries, each having an emf of 1.5 V, connected in series with a bulb having resistance 17 Ω. If the internal resistance of the batteries is negligible, what power is delivered to the bulb?
Problem 46b
A typical small flashlight contains two batteries, each having an emf of 1.5 V, connected in series with a bulb having resistance 17 Ω. If the batteries last for 5.0 h, what is the total energy delivered to the bulb?
Problem 46c
A typical small flashlight contains two batteries, each having an emf of 1.5 V, connected in series with a bulb having resistance 17 Ω. The resistance of real batteries increases as they run down. If the initial internal resistance is negligible, what is the combined internal resistance of both batteries when the power to the bulb has decreased to half its initial value?
Problem 49
Pure silicon at room temperature contains approximately 1.0 × 1016 free electrons per cubic meter. (a) Referring to Table 25.1, calculate the mean free time t for silicon at room temperature. (b) Your answer in part (a) is much greater than the mean free time for copper given in Example 25.11. Why, then, does pure silicon have such a high resistivity compared to copper?