Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Ethers
Ethers are a class of organic compounds characterized by an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula R-O-R', where R and R' represent the hydrocarbon chains. Ethers are known for their relatively low reactivity and are commonly used as solvents in organic chemistry due to their ability to dissolve a wide range of substances.
Recommended video:
Nomenclature of Ethers
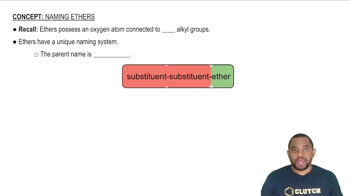
The nomenclature of ethers follows specific rules set by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). Ethers are typically named by identifying the two alkyl or aryl groups attached to the oxygen atom, followed by the word 'ether.' For example, in diethyl ether, the two ethyl groups are named first, indicating their connection through the oxygen atom.
Recommended video:
Common Ethers
Some common examples of ethers include diethyl ether, which is often used as a solvent, and methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE), used as a fuel additive. Recognizing these common ethers and their applications can help in understanding their significance in both laboratory and industrial settings. Familiarity with these examples aids in the identification and naming of various ethers in chemical contexts.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance