Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
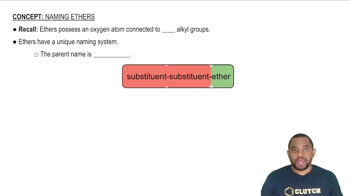
Ethers
Ethers are a class of organic compounds characterized by an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. The general formula for ethers is R-O-R', where R and R' represent the hydrocarbon chains. Ethers are known for their relatively low reactivity and are commonly used as solvents in organic chemistry.
Recommended video:
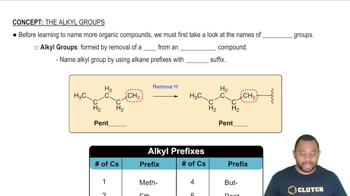
Alkyl Groups
Alkyl groups are derived from alkanes by removing one hydrogen atom, resulting in a functional group that can bond with other atoms. They are typically represented as 'R' in chemical formulas and can vary in size and structure, influencing the properties of the compounds they form. In the case of methyl hexyl ether, the methyl group (CH3) and hexyl group (C6H13) are the two alkyl components.
Recommended video:
Structural Representation
Structural representation in chemistry involves depicting the arrangement of atoms within a molecule, including bonds and functional groups. This can be done using various methods, such as Lewis structures, condensed formulas, or skeletal formulas. For methyl hexyl ether, understanding how to represent the ether linkage (the oxygen atom connecting the two alkyl groups) is crucial for accurately drawing its structure.
Recommended video: