Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
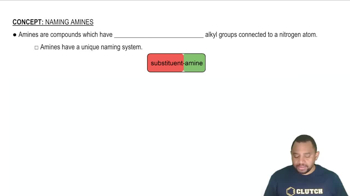
Amines
Amines are organic compounds derived from ammonia (NH3) by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms with alkyl or aryl groups. They can be classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary based on the number of carbon-containing groups attached to the nitrogen atom. Understanding the structure of amines is crucial for naming them correctly.
Recommended video:
Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
The nomenclature of organic compounds follows specific rules set by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). For amines, the naming involves identifying the longest carbon chain attached to the nitrogen and using suffixes or prefixes to denote the presence of the amine functional group. Familiarity with these rules is essential for accurately naming amines.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Organic Chemistry
Functional Groups
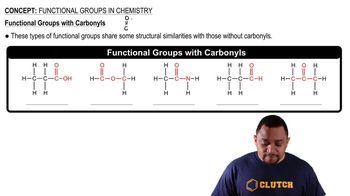
Functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. In the case of amines, the amino group (-NH2) is the functional group that defines their chemical behavior. Recognizing functional groups helps in understanding the reactivity and properties of organic compounds.
Recommended video:
Carbonyl Functional Groups
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance