Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Amines
Amines are organic compounds derived from ammonia (NH3) by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms with alkyl or aryl groups. They can be classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary based on the number of carbon-containing groups attached to the nitrogen atom. Amines are characterized by their basicity and can participate in hydrogen bonding, influencing their physical properties.
Recommended video:
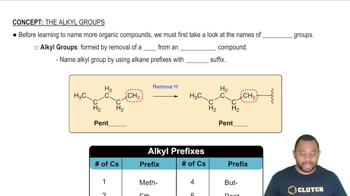
Alkyl Groups
Alkyl groups are hydrocarbon substituents derived from alkanes by removing one hydrogen atom. They are denoted by the formula CnH2n+1, where 'n' represents the number of carbon atoms. In the case of butylethylamine, the butyl group (C4H9) and ethyl group (C2H5) are the two alkyl groups attached to the nitrogen atom, which define the structure of the amine.
Recommended video:
Structural Representation
Structural representation in chemistry involves depicting the arrangement of atoms within a molecule. For amines, this includes showing the nitrogen atom bonded to its alkyl groups and any hydrogen atoms. Understanding how to draw these structures accurately is essential for visualizing molecular interactions and predicting chemical behavior.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance