Ch.5 - Periodicity & Electronic Structure of Atoms
 Back
BackProblem 1
Which wave corresponds to higher energy radiation? (LO 5.1) (a)
(b)
- What is the energy (in kJ) of one mole of photons of ultraviolet light with a wavelength of 85 nm? (LO 5.3) (a) 1.4 * 10-6 kJ (b) 1.4 * 103 kJ (c) 2.4 * 1014 kJ (d) 2.4 * 10-15 kJ
Problem 3
- Which type of electromagnetic radiation will cause the greatest number of electrons to be ejected from zinc metal with a work function of 350 kJ/mol? (LO 5.4, 5.5) (a) Dim light with a wavelength of 320 nm (b) Dim light with a wavelength of 360 nm (c) Bright light with a wavelength of 360 nm (d) Bright light with a wavelength of 375 nm
Problem 4
Problem 6
When a copper salt such as Cu(NO3)2 is burned in a flame, a blue-green color is emitted. Which figure represents the emission spectrum for the element copper? (LO 5.6)? (a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
- Which arrow in the energy diagram for an atom represents the absorption of light with the shortest wavelength? (LO 5.7)
Problem 7

- Calculate the wavelength in nm of the light emitted when an electron makes a transition from an orbital in n = 5 to an orbital in n = 2 in the hydrogen atom. (LO 5.8) (a) 2.31 * 10-3 nm (b) 4.34 * 10-2 nm (c) 231 nm (d) 434 nm
Problem 8
- What are the possible values of n, l, and ml for an electron in a 5p orbital? (LO 5.12)
Problem 10
- What are the possible values of n, l, and ml for the orbital shown? (LO 5.13)
Problem 11
Problem 26a
Two electromagnetic waves are represented below. (
(a) Which wave has the greater intensity?
Problem 26c
Two electromagnetic waves are represented below.
(c) Which wave represents yellow light, and which represents infrared radiation?
- Identify each of the following orbitals, and give n and l quantum numbers for each. (a)
Problem 28
(b)
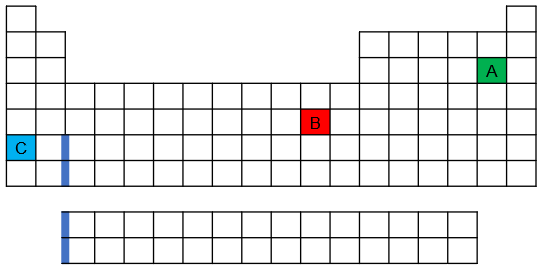
- Where on the blank outline of the periodic table do elements that meet the following descriptions appear? (c) Elements with electrons whose largest principal quantum number is n = 4
Problem 29

- One of the elements shown on the following periodic table has an anomalous ground-state electron configuration. Which is it—red, blue, or green—and why?
Problem 30
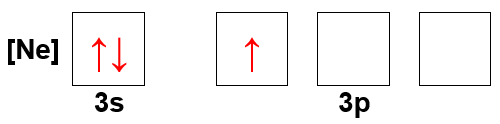
- What atom has the following orbital-filling diagram?
Problem 31
Problem 33
Which of the following three spheres represents a Ca atom, which an Sr atom, and which a Br atom?

- Which has the higher frequency, red light or violet light? Which has the longer wavelength? Which has the greater energy?
Problem 34
- Which has the higher frequency, infrared light or ultraviolet light? Which has the longer wavelength? Which has the greater energy?
Problem 35
- The Hubble Space Telescope detects electromagnetic energy in the wavelength range 1.15 * 10-7 m to 2.0 * 10-6 m. What region of the electromagnetic spectrum is found completely within this range? What regions fall partially in this range?
Problem 36
- The Green Bank Telescope in West Virginia—the world's largest steerable radio telescope—detects frequencies from 290 MHz to 90 GHz. What region or regions of the electro-magnetic spectrum are found completely or partially within its detection range?
Problem 37
- What is the frequency of a microwave with l = 4.33 * 10-3 m?
Problem 39
- A certain cellular telephone transmits at a frequency of 825 MHz and receives at a frequency of 875 MHz. (a) What is the wavelength of the transmitted signal in cm?
Problem 40
- (b) Fiber optic cable is available in 12 km lengths. How long will it take for a signal to travel that distance assuming that the speed of light in the cable is the same as in a vacuum?
Problem 41
- Calculate the energies of the following waves in kilojoules per mole, and tell which member of each pair has the higher value. (a) An FM radio wave at 99.5 MHz and an AM radio wave at 1150 kHz
Problem 42
- What is the energy of each of the following photons in kilojoules per mole? (a) v = 5.97 * 1019 s-1 (b) v = 1.26 * 106 s-1 (c)
Problem 45
= 2.57 * 102 m - (c) What type of electromagnetic radiation are these photons?
Problem 46
- (c) What is the color of the light with
Problem 47
= 450 nm? - The work function of cesium metal is 188 kJ/mol, which corresponds to light with a wavelength of 637 nm. Which of the following will cause the smallest number of electrons to be ejected from cesium? (a) High-amplitude wave with a wavelength of 500 nm (b) Low-amplitude wave with a wavelength of 500 nm (c) High-amplitude wave with a wavelength of 650 nm (d) Low-amplitude wave with a wavelength of 650 nm
Problem 52
- The work function of calcium metal is kJ/mol, which corresponds to light with a wavelength of 432 nm. Which of the following will cause the largest number of electrons to be ejected from cesium? (a) High-amplitude wave with a wavelength of 400 nm (b) Low-amplitude wave with a wavelength of 400 nm (c) High-amplitude wave with a wavelength of 450 nm (d) Low-amplitude wave with a wavelength of 450 nm
Problem 53
- The work function of silver metal is 436 kJ/mol. What frequency of light is needed to eject electrons from a sample of silver?
Problem 54
- Cesium metal is frequently used in photoelectric cells because the amount of energy necessary to eject electrons from a cesium surface is relatively small—only 206.5 kJ/mol. What wavelength of light in nanometers does this correspond to?
Problem 55

