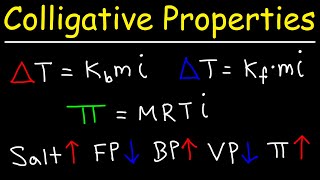
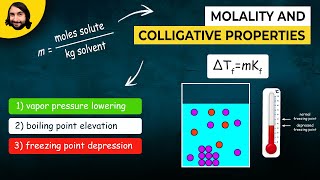
14. Solutions
Boiling Point Elevation
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
An ethylene glycol solution contains 25.2 g of ethylene glycol (C2H6O2) in 99.5 mL of water. Determine the change in boiling point. Assume a density of 1.00 g/mL for water.
2067views1comments - Multiple Choice
Pure water boils at 100°C. What is the new boiling point of water after the addition of 13.12 g aluminum chloride, AlCl3, to 615 g water?
2683views6rank - Multiple Choice
What is the molality of glucose in an aqueous solution if the boiling point of the solution is 103.15°C?
1751views - Multiple Choice
Carbon dioxide is dissolved in 722 mL of benzene with a density of 1.59 g/mL. What mass of carbon dioxide would you add to make the boiling point of the solution 104.7°C? (BP of benzene = 80.1 °C)
1492views4rank4comments - Open Question
Determine the boiling point of a solution that contains 78.8 g of naphthalene (C10H8, molar mass = 128.16 g/mol) dissolved in 722 mL of benzene (d = 0.877 g/ml). Pure benzene has a boiling point of 80.1°C and a boiling point elevation constant of 2.53°C/m.
1085views - Open Question
A solution of toluene (C₇H₈) in 301 g of cyclohexane (C₆H₁₂) has a boiling point of 90.30°C. what quantity in moles of toluene are in the solution? (for cyclohexane kb = 2.92°C/m, normal boiling point, Tb = 80.90°C)
1126views - Open Question
Determine the boiling point of a solution that contains 78.8 g of naphthalene (C10H8, molar mass = 128.16 g/mol) dissolved in 722 ml of benzene (d = 0.877 g/ml). Pure benzene has a boiling point of 80.1°C and a boiling point elevation constant of 2.53°C/m.
1048views