Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Epigenetics
Epigenetics refers to the study of heritable changes in gene expression that do not involve alterations to the underlying DNA sequence. These changes can be influenced by various factors, including environmental conditions, lifestyle, and developmental stages. Epigenetic modifications, such as DNA methylation and histone modification, can affect how genes are turned on or off, thereby impacting an organism's phenotype.
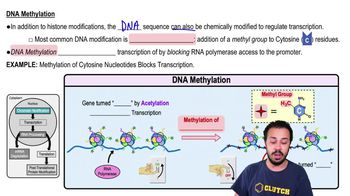
DNA Methylation
DNA methylation is a specific epigenetic mechanism where methyl groups are added to the DNA molecule, typically at cytosine bases. This modification can inhibit gene expression by preventing the binding of transcription factors or recruiting proteins that compact the DNA, making it less accessible for transcription. Methylation patterns can be stable and passed down through generations, influencing traits in offspring without changing the DNA sequence itself.
Recommended video:
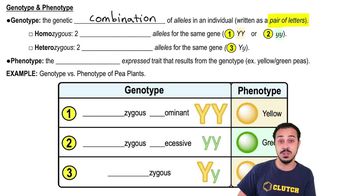
Phenotype
Phenotype refers to the observable physical and physiological traits of an organism, which result from the interaction of its genotype with the environment. This includes characteristics such as morphology, development, biochemical properties, and behavior. Epigenetic changes, like those caused by DNA methylation, can lead to variations in phenotype, demonstrating how environmental factors can influence genetic expression and trait development.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance