Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Rami Communicantes
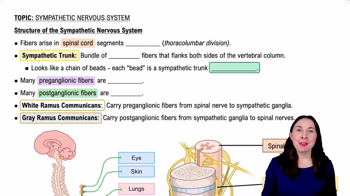
Rami communicantes are small nerve fibers that connect the spinal nerves to the sympathetic trunk. They are involved in the autonomic nervous system, specifically in relaying signals between the central nervous system and peripheral organs. The white rami communicantes specifically carry preganglionic sympathetic fibers from the spinal cord to the sympathetic ganglia.
Recommended video:
Structure of the Sympathetic Nervous System
Preganglionic vs. Postganglionic Fibers
Preganglionic fibers are the axons of neurons that originate in the central nervous system and extend to a ganglion, where they synapse with postganglionic neurons. Postganglionic fibers then carry signals from the ganglion to the target organs. Understanding the distinction between these two types of fibers is crucial for comprehending the pathways of the autonomic nervous system.
Recommended video:
Sympathetic Nervous System
The sympathetic nervous system is a part of the autonomic nervous system that prepares the body for 'fight or flight' responses during stressful situations. It increases heart rate, dilates airways, and inhibits digestion, among other functions. The fibers involved in this system, particularly the preganglionic sympathetic fibers, are essential for initiating these physiological changes.
Recommended video:
Sympathetic Nervous System Example 3
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance