Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Sympathetic Nervous System
The sympathetic nervous system is a part of the autonomic nervous system responsible for the body's 'fight or flight' response. It prepares the body for stressful situations by increasing heart rate, dilating airways, and redirecting blood flow to essential organs. Understanding its role is crucial for analyzing how collateral sympathetic ganglia function in innervating various organs.
Recommended video:
Sympathetic Nervous System Example 3
Collateral Sympathetic Ganglia
Collateral sympathetic ganglia are clusters of nerve cell bodies located outside the spinal cord that serve as relay points for sympathetic nerve fibers. They innervate various organs, including those in the abdomen and thorax, by transmitting signals that regulate functions such as digestion and heart rate. Their involvement in organ innervation is key to answering the question.
Recommended video:
Sympathetic Nervous System Example 5
Organ Innervation
Organ innervation refers to the supply of nerves to an organ, allowing for communication between the nervous system and the organ. In the context of the sympathetic nervous system, this involves the regulation of involuntary functions such as heart rate, blood pressure, and glandular secretion. Recognizing which organs are innervated by collateral sympathetic ganglia is essential for determining the correct answer to the question.
Recommended video:
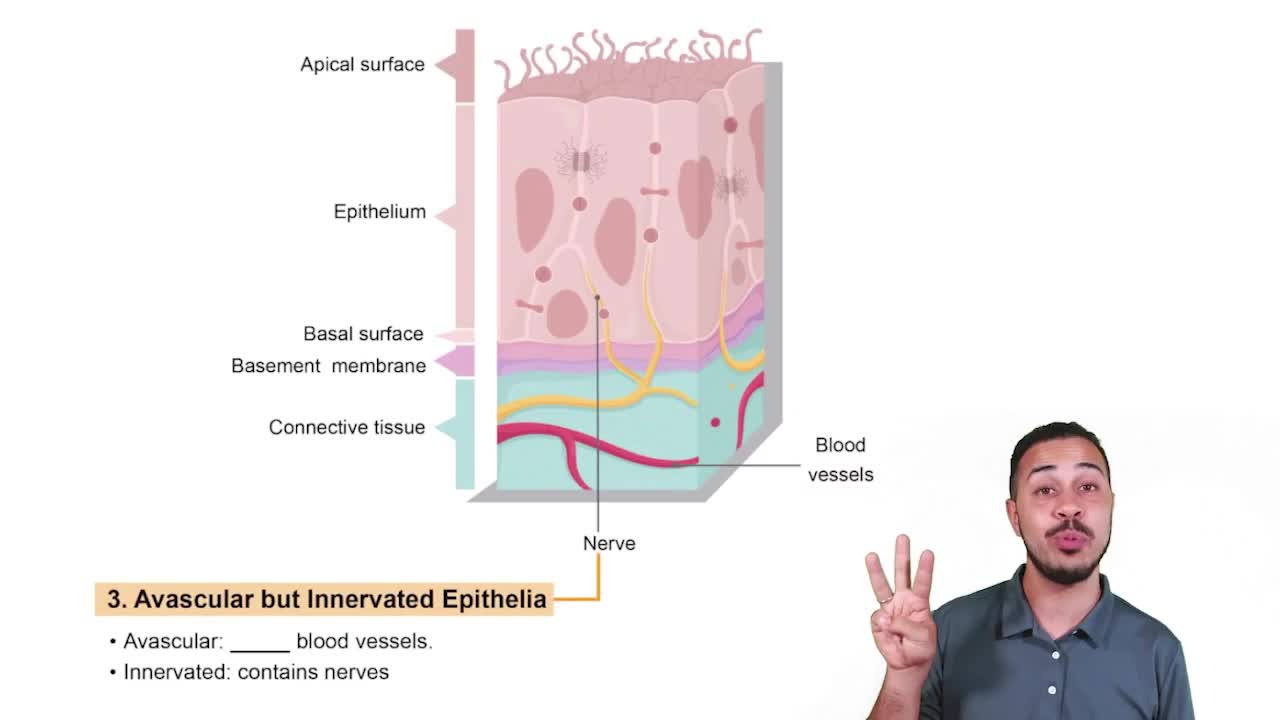
Characteristic 3: Avascular but Innervated