Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Focal Length
Focal length is the distance from the lens to the point where parallel rays of light converge or appear to diverge. In microscopes, the focal lengths of the objective and eyepiece lenses are crucial for determining how the lenses will magnify the image. A shorter focal length typically results in greater magnification, which is essential for resolving fine details in microscopic images.
Recommended video:
Spinning on a string of variable length
Angular Magnification
Angular magnification is a measure of how much larger an object appears when viewed through a microscope compared to the naked eye. It is calculated as the ratio of the angle subtended by the image at the eye to the angle subtended by the object at the same position. This concept is vital for understanding how effectively a microscope can enhance the visibility of small objects.
Recommended video:
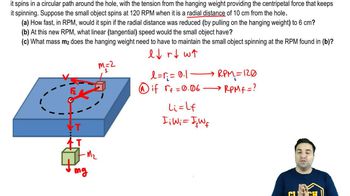
Conservation of Angular Momentum
Compound Microscope
A compound microscope uses two or more lenses to achieve higher magnification and resolution. The objective lens creates a magnified image of the specimen, which is then further magnified by the eyepiece. Understanding the arrangement and function of these lenses is essential for calculating the overall magnification and resolving power of the microscope.
Recommended video:
Microscopic View of Current