Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Ideal Gas Law
The Ideal Gas Law is a fundamental equation in thermodynamics that relates the pressure (P), volume (V), number of moles (n), and temperature (T) of an ideal gas. It is expressed as PV = nRT, where R is the ideal gas constant. This law allows us to calculate the number of moles of gas when the other variables are known, making it essential for solving problems involving gas behavior.
Recommended video:
Ideal Gases and the Ideal Gas Law
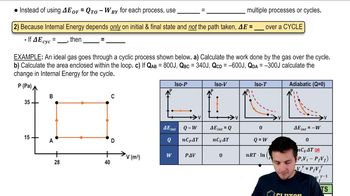
Pressure-Volume Relationship
The pressure-volume relationship describes how the pressure of a gas changes with its volume at constant temperature. According to Boyle's Law, for a given amount of gas at constant temperature, the pressure is inversely proportional to the volume. This relationship is illustrated in the provided graph, where the curve shows how pressure decreases as volume increases, which is crucial for understanding the gas's behavior during the process depicted.
Recommended video:
Pressure and Atmospheric Pressure
Thermodynamic Processes
Thermodynamic processes refer to the changes in state variables of a gas, such as pressure, volume, and temperature, during a physical transformation. These processes can be isothermal, adiabatic, isobaric, or isochoric, depending on the conditions maintained. Understanding the type of process is vital for applying the Ideal Gas Law correctly and determining the number of moles of gas involved in the transformation shown in the graph.
Recommended video:
Properties of Cyclic Thermodynamic Processes