Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Ideal Gas Law
The Ideal Gas Law relates the pressure, volume, temperature, and number of moles of a gas through the equation PV = nRT. This law is fundamental for understanding gas behavior under varying conditions, allowing us to calculate one property if the others are known. In this problem, it will help determine the final volume after the gas undergoes changes in temperature and pressure.
Recommended video:
Ideal Gases and the Ideal Gas Law
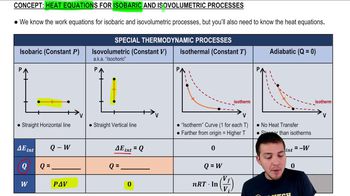
Isobaric Process
An isobaric process is a thermodynamic process in which the pressure remains constant while the volume and temperature may change. In this scenario, the gas first undergoes an isobaric process that doubles its absolute temperature, which directly affects its volume according to the Ideal Gas Law. Understanding this concept is crucial for calculating the new volume after the temperature change.
Recommended video:
Heat Equations for Isobaric & Isovolumetric Processes
Isothermal Process
An isothermal process occurs at a constant temperature, meaning that any change in pressure will result in a corresponding change in volume, as described by Boyle's Law (PV = constant). In this problem, after the isobaric process, the gas undergoes an isothermal process that halves the pressure, which will further affect the volume. Recognizing how these processes interact is key to finding the final volume of the gas.
Recommended video:
Entropy & Ideal Gas Processes