Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Ideal Gas Law
The Ideal Gas Law relates the pressure, volume, temperature, and number of moles of a gas through the equation PV = nRT. In this scenario, understanding how pressure and volume interact is crucial, especially since the process is isobaric (constant pressure), allowing us to focus on the relationship between volume and temperature.
Recommended video:
Ideal Gases and the Ideal Gas Law
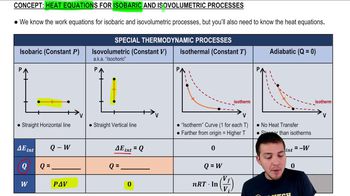
Isobaric Process
An isobaric process is one in which the pressure remains constant while the volume and temperature of the gas change. For this question, since the pressure is constant at 3.0 atm, we can use the initial and final volumes and temperatures to determine the new volume after the gas expands.
Recommended video:
Heat Equations for Isobaric & Isovolumetric Processes
Charles's Law
Charles's Law states that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature when pressure is held constant. This principle is essential for calculating the final volume of nitrogen gas after the isobaric expansion, as the temperature will increase when the volume triples, allowing us to find the new volume using the initial conditions.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance