DRAW IT What nutritional type is a colorless microbe that uses the Calvin-Benson cycle, uses H₂ as the electron donor to its ETC, and uses elemental S as the final electron acceptor in the ETC?
DRAW IT Using the following diagrams, show each of the following:
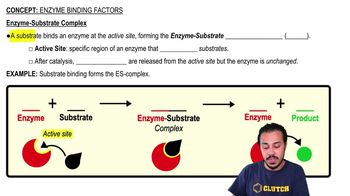
a. where the substrate will bind
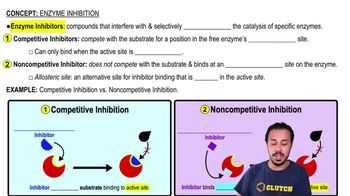
b. where the competitive inhibitor will bind
c. where the noncompetitive inhibitor will bind
d. which of the four elements could be the inhibitor in feedback inhibition
e. What effect will the reactions in (a), (b), and (c) have?
<IMAGE>
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Enzyme-Substrate Interaction
Competitive and Noncompetitive Inhibition
Feedback Inhibition

Which substance in the following reaction is being reduced?
<IMAGE>
a. acetaldehyde
b. NADH
c. ethanol
d. NAD⁺
Use the following choices to answer questions 7–10.
a. E. coli growing in glucose broth at 35℃ with O₂ for 5 days
b. E. coli growing in glucose broth at 35℃ without O₂ for 5 days
c. both a and b
d. neither a nor b
Which culture uses the most glucose?
Which of the following reactions produces the most molecules of ATP during aerobic metabolism?
a. glucose → glucose 6-phosphate
b. phosphoenolpyruvic acid → pyruvic acid
c. glucose → pyruvic acid
d. acetyl CoA → CO₂ + H₂O
e. succinic acid → fumaric acid
DRAW IT An enzyme and substrate are combined. The rate of reaction begins as shown in the following graph. To complete the graph, show the effect of increasing substrate concentration on a constant enzyme concentration. Show the effect of increasing temperature.
<IMAGE>
Which of the following processes does not generate ATP?
a. photophosphorylation
b. the Calvin-Benson cycle
c. oxidative phosphorylation
d. substrate-level phosphorylation
e. All of the above generate ATP
