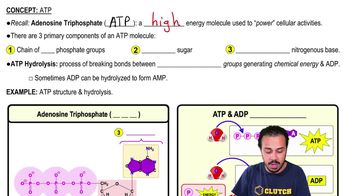
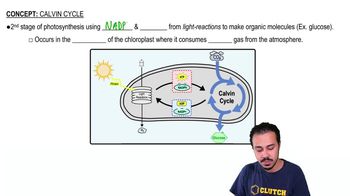
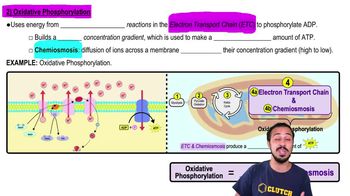
DRAW IT Using the following diagrams, show each of the following:
a. where the substrate will bind
b. where the competitive inhibitor will bind
c. where the noncompetitive inhibitor will bind
d. which of the four elements could be the inhibitor in feedback inhibition
e. What effect will the reactions in (a), (b), and (c) have?
<IMAGE>