Which of the following processes does not generate ATP?
a. photophosphorylation
b. the Calvin-Benson cycle
c. oxidative phosphorylation
d. substrate-level phosphorylation
e. All of the above generate ATP
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
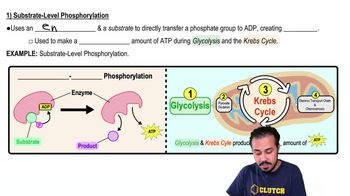
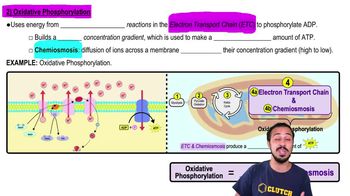
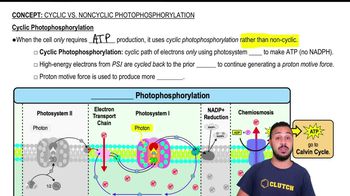
Which of the following processes does not generate ATP?
a. photophosphorylation
b. the Calvin-Benson cycle
c. oxidative phosphorylation
d. substrate-level phosphorylation
e. All of the above generate ATP
Which of the following compounds has the greatest amount of energy for a cell?
a. CO₂
b. ATP
c. glucose
d. O₂
e. lactic acid
Define oxidation-reduction, and differentiate the following terms:
a. aerobic and anaerobic respiration
b. respiration and fermentation
c. cyclic and noncyclic photophosphorylation
Which of the following is the best definition of the Krebs cycle?
a. the oxidation of pyruvic acid
b. the way cells produce CO₂
c. a series of chemical reactions in which NADH is produced from the oxidation of pyruvic acid
d. a method of producing ATP by phosphorylating ADP
e. a series of chemical reactions in which ATP is produced from the oxidation of pyruvic acid
All of the energy-producing biochemical reactions that occur in cells, such as photophosphorylation and glycolysis, are ________ reactions.
Which of the following is the best definition of cellular respiration?
a. a sequence of redox reactions with O₂ as the final electron acceptor
b. a sequence of redox reactions with the final electron acceptor from the environment
c. a method of generating ATP
d. the complete oxidation of glucose to CO₂ and H₂O
e. a series of reactions in which pyruvic acid is oxidized to CO₂ and H₂O