Define oxidation-reduction, and differentiate the following terms:
a. aerobic and anaerobic respiration
b. respiration and fermentation
c. cyclic and noncyclic photophosphorylation
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


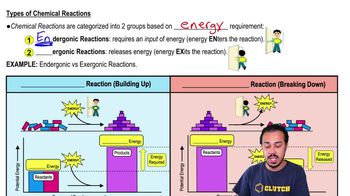
Define oxidation-reduction, and differentiate the following terms:
a. aerobic and anaerobic respiration
b. respiration and fermentation
c. cyclic and noncyclic photophosphorylation
There are three mechanisms for the phosphorylation of ADP to produce ATP. Write the name of the mechanism that describes each of the reactions in the following table.
<IMAGE>
Which of the following is the best definition of the Krebs cycle?
a. the oxidation of pyruvic acid
b. the way cells produce CO₂
c. a series of chemical reactions in which NADH is produced from the oxidation of pyruvic acid
d. a method of producing ATP by phosphorylating ADP
e. a series of chemical reactions in which ATP is produced from the oxidation of pyruvic acid
Which of the following is the best definition of cellular respiration?
a. a sequence of redox reactions with O₂ as the final electron acceptor
b. a sequence of redox reactions with the final electron acceptor from the environment
c. a method of generating ATP
d. the complete oxidation of glucose to CO₂ and H₂O
e. a series of reactions in which pyruvic acid is oxidized to CO₂ and H₂O
Fill in the following table with the carbon source and energy source of each type of organism.
<IMAGE>
Use the following choices to answer questions 7–10.
a. E. coli growing in glucose broth at 35℃ with O₂ for 5 days
b. E. coli growing in glucose broth at 35℃ without O₂ for 5 days
c. both a and b
d. neither a nor b
Which culture produces the most lactic acid?