All of the energy-producing biochemical reactions that occur in cells, such as photophosphorylation and glycolysis, are ________ reactions.
Use the following choices to answer questions 7–10.
a. E. coli growing in glucose broth at 35℃ with O₂ for 5 days
b. E. coli growing in glucose broth at 35℃ without O₂ for 5 days
c. both a and b
d. neither a nor b
Which culture produces the most lactic acid?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Lactic Acid Fermentation
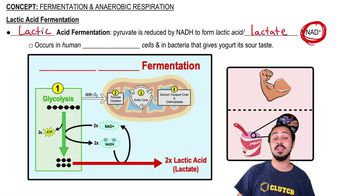
Aerobic vs. Anaerobic Metabolism

Effect of Oxygen on Metabolite Production
Which of the following is the best definition of cellular respiration?
a. a sequence of redox reactions with O₂ as the final electron acceptor
b. a sequence of redox reactions with the final electron acceptor from the environment
c. a method of generating ATP
d. the complete oxidation of glucose to CO₂ and H₂O
e. a series of reactions in which pyruvic acid is oxidized to CO₂ and H₂O
Fill in the following table with the carbon source and energy source of each type of organism.
<IMAGE>
Write your own definition of the chemiosmotic mechanism of ATP generation. On Figure 5.16, mark the following using the appropriate letter:
a. the acidic side of the membrane
b. the side with a positive electrical charge
c. potential energy
d. kinetic energy
Use the following choices to answer questions 7–10.
a. E. coli growing in glucose broth at 35℃ with O₂ for 5 days
b. E. coli growing in glucose broth at 35℃ without O₂ for 5 days
c. both a and b
d. neither a nor b
Which culture produces the most ATP?
Why must NADH be reoxidized? How does this happen in an organism that uses respiration? Fermentation?
