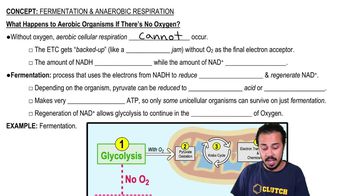
DRAW IT The artificial sweetener aspartame, or NutraSweet®, is made by joining aspartic acid to methylated phenylalanine, as shown in the following.
<IMAGE>
a. What types of molecules are aspartic acid and phenylalanine?
b. What direction is the hydrolysis reaction (left to right or right to left)?
c. What direction is the dehydration synthesis reaction?
d. Circle the atoms involved in the formation of water.
e. Identify the peptide bond.