There are different tRNAs for each amino acid. What is one major way to differentiate among the tRNAs for each amino acid?
Write the complementary sequence of bases for each DNA strand shown next.
a. 5′T-A-T-A-C-T-G 3′
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
DNA Structure
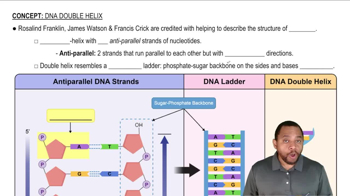
Complementary Base Pairing

5' and 3' Ends of DNA Strands
Insulin is synthesized as preproinsulin, which has 81 amino acids. How many heterocyclic bases must be present in the informational DNA strand to code for preproinsulin (assuming no introns are present)?
Suppose that 22% of the nucleotides of a DNA molecule are deoxyadenosine and during replication the relative amounts of available deoxynucleoside triphosphates are 22% dATP, 22% dCTP, 28% dGTP, and 28% dTTP. What deoxynucleoside triphosphate is limiting to the replication? Explain.
Draw the structures of adenine and uracil (which replaces thymine in RNA), and show the hydrogen bonding that occurs between them.
(a) DNA and RNA, like proteins, can be denatured to produce unfolded or uncoiled strands. Heating DNA to what is referred to as its “melting temperature” denatures it (the two strands of the double helix become separated). Why does a longer strand of DNA have a higher melting temperature than a shorter one?
a. What is meant by the term base pairing?
