Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Sex Chromosome Function
In humans, sex determination is primarily influenced by the presence of the Y chromosome. The SRY gene located on the Y chromosome triggers male development, while its absence leads to female development. The X chromosomes carry genes that are not directly involved in determining sex but are essential for various biological functions.
Recommended video:
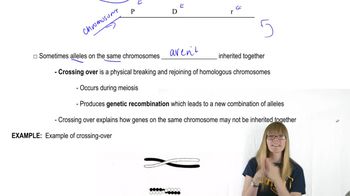
Crossover and Genetic Mapping
Crossover refers to the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during meiosis, which can result in new allele combinations. Missing expected crossover phenotypes can occur due to genetic linkage, where genes are located close together on the same chromosome, reducing the likelihood of recombination. Genetic mapping involves determining the distance between loci based on crossover frequencies.
Recommended video:
Map Distance Calculation
Map distance is a measure of the relative distance between genes on a chromosome, typically expressed in centimorgans (cM). It is calculated based on the frequency of recombination events; a higher frequency indicates greater distance. By analyzing the data from crossover events, one can estimate the map distances between loci, aiding in the understanding of genetic linkage and inheritance patterns.
Recommended video: