
The study of biochemical mutants in organisms such as Neurospora has demonstrated that some pathways are branched. The data shown in the following table illustrate the branched nature of the pathway resulting in the synthesis of thiamine:
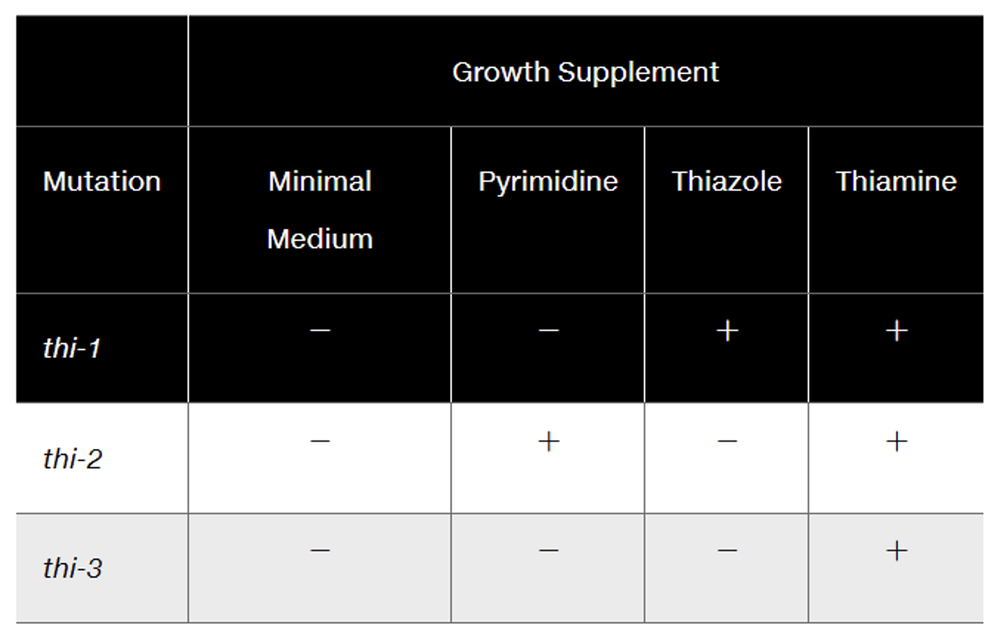
Why don't the data support a linear pathway? Can you postulate a pathway for the synthesis of thiamine in Neurospora?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Branched Pathways in Metabolism

Mutations and Their Effects

Supplementation and Growth Conditions

The synthesis of flower pigments is known to be dependent on enzymatically controlled biosynthetic pathways. For the crosses shown here, postulate the role of mutant genes and their products in producing the observed phenotypes:
P₁: white strain A × white strain B
F₁: all purple
F₂: 9/16purple: 7/16 white
The synthesis of flower pigments is known to be dependent on enzymatically controlled biosynthetic pathways. For the crosses shown here, postulate the role of mutant genes and their products in producing the observed phenotypes:
P₁: white × pink
F₁: all purple
F₂: 9/16 purple: 3/16 pink: 4/16 white
Explain why the one-gene:one-enzyme concept is not considered totally accurate today.
Using sickle-cell anemia as an example, describe what is meant by a molecular or genetic disease. What are the similarities and dissimilarities between this type of a disorder and a disease caused by an invading microorganism?
