Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Aldehydes
Aldehydes are organic compounds characterized by the presence of a carbonyl group (C=O) at the end of a carbon chain. The general formula for aldehydes is RCHO, where R represents a hydrocarbon group. Common examples include formaldehyde and acetaldehyde. Aldehydes are known for their distinctive odors and are often used in the production of various chemicals and as preservatives.
Recommended video:
Rules for Naming Aldehydes
Ketones
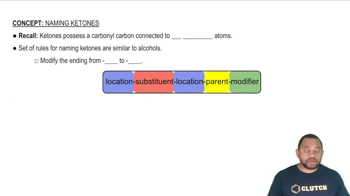
Ketones are organic compounds that contain a carbonyl group (C=O) located within a carbon chain, specifically between two carbon atoms. The general formula for ketones is RC(=O)R', where R and R' can be the same or different hydrocarbon groups. Acetone is a well-known example of a ketone, commonly used as a solvent. Ketones are important in various chemical reactions and industrial applications.
Recommended video:
Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
The nomenclature of organic compounds follows specific rules set by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). For aldehydes, the suffix '-al' is used, while for ketones, the suffix '-one' is applied. The naming process involves identifying the longest carbon chain containing the functional group, numbering the chain to give the functional group the lowest possible number, and then applying the appropriate suffix based on the compound type.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Organic Chemistry