Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Alcohol Functional Group
Alcohols are organic compounds characterized by the presence of one or more hydroxyl (-OH) groups attached to a carbon atom. This functional group is responsible for the unique chemical properties of alcohols, including their reactivity in various chemical reactions such as oxidation, dehydration, and substitution.
Recommended video:
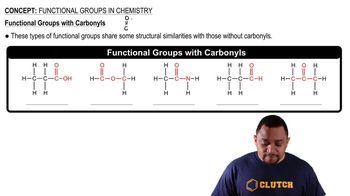
Carbonyl Functional Groups
Types of Reactions Involving Alcohols
Alcohols can undergo several types of reactions, including oxidation, where they are converted to aldehydes or ketones, and dehydration, which leads to the formation of alkenes. Understanding these reactions is crucial for predicting the products formed when alcohols react under different conditions.
Recommended video:
Alcohol Reactions: Dehydration Reactions
Reaction Mechanisms
The mechanisms of alcohol reactions involve step-by-step processes that describe how reactants are transformed into products. Familiarity with these mechanisms, such as nucleophilic substitution or elimination, helps in understanding the pathways and intermediates involved, which ultimately determines the products formed in each reaction.
Recommended video:
Reaction Mechanism Overview
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance