Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Alcohol Functional Group
Alcohols are organic compounds characterized by the presence of one or more hydroxyl (-OH) functional groups. This functional group is responsible for the chemical properties of alcohols, including their ability to form hydrogen bonds, which affects their boiling points and solubility in water.
Recommended video:
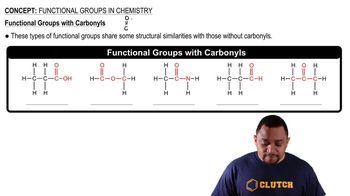
Carbonyl Functional Groups
Nomenclature of Alcohols
The naming of alcohols follows specific IUPAC rules, where the longest carbon chain containing the hydroxyl group is identified, and the suffix '-ol' is added to the root name. The position of the hydroxyl group is indicated by a number, ensuring clarity in the structure of the compound.
Recommended video:
Rules for Naming Alcohols
Classification of Alcohols
Alcohols can be classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary based on the carbon atom to which the hydroxyl group is attached. A primary alcohol has the -OH group on a carbon bonded to one other carbon, a secondary alcohol is bonded to two, and a tertiary alcohol is bonded to three, influencing their reactivity and properties.
Recommended video:
Rules for Naming Alcohols

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance