Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Alcohol Functional Group
Alcohols are organic compounds characterized by the presence of one or more hydroxyl (-OH) groups attached to a carbon atom. This functional group is responsible for the chemical properties of alcohols, including their ability to form hydrogen bonds, which affects their boiling points and solubility in water.
Recommended video:
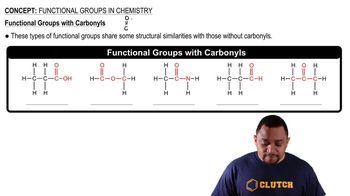
Carbonyl Functional Groups
IUPAC Nomenclature
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) nomenclature provides a systematic method for naming organic compounds. For alcohols, the name is derived from the longest carbon chain containing the -OH group, with the suffix '-ol' indicating the presence of the alcohol functional group, and the position of the -OH group is indicated by a number.
Recommended video:
Structural Isomerism
Structural isomerism occurs when compounds have the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements of atoms. In the case of alcohols, variations in the carbon skeleton or the position of the -OH group can lead to different isomers, each with distinct properties and names, which is crucial for accurately identifying and naming the alcohol in the given structure.
Recommended video:
Isomerism in Coordination Complexes Example

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance