(a) Draw a picture that represents a crystalline solid at the atomic level.
Ch.12 - Solids and Modern Materials
Chapter 12, Problem 22c
Two patterns of packing two different circles of the same size are shown here. For each structure (c) determine the type of two-dimensional lattice (from Figure 12.4). (i)

(ii)
![]()
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Observe the two packing patterns of circles labeled I and II.
Identify the type of two-dimensional lattice for pattern I. Notice that the circles are arranged in a hexagonal pattern, where each circle is surrounded by six others.
Identify the type of two-dimensional lattice for pattern II. Notice that the circles are arranged in a rectangular pattern, where each circle is surrounded by four others.
Refer to Figure 12.4 in your textbook to match these observations with the corresponding lattice types.
Conclude that pattern I corresponds to a hexagonal lattice and pattern II corresponds to a rectangular lattice.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Two-Dimensional Lattices
A two-dimensional lattice is a regular arrangement of points in a plane, where each point represents the position of a particle, such as atoms or molecules. The arrangement can be characterized by its symmetry and the shape of the unit cell, which is the smallest repeating unit that defines the entire lattice structure. Common types of two-dimensional lattices include square, rectangular, and hexagonal lattices.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Lattice Energy
Crystalline Structures
Crystalline structures are ordered arrangements of atoms or molecules in a solid, resulting in distinct geometric shapes. In two dimensions, these structures can be visualized as patterns of circles or spheres that represent the particles. The packing efficiency and arrangement of these particles determine the properties of the material, such as density and stability.
Recommended video:
Guided course
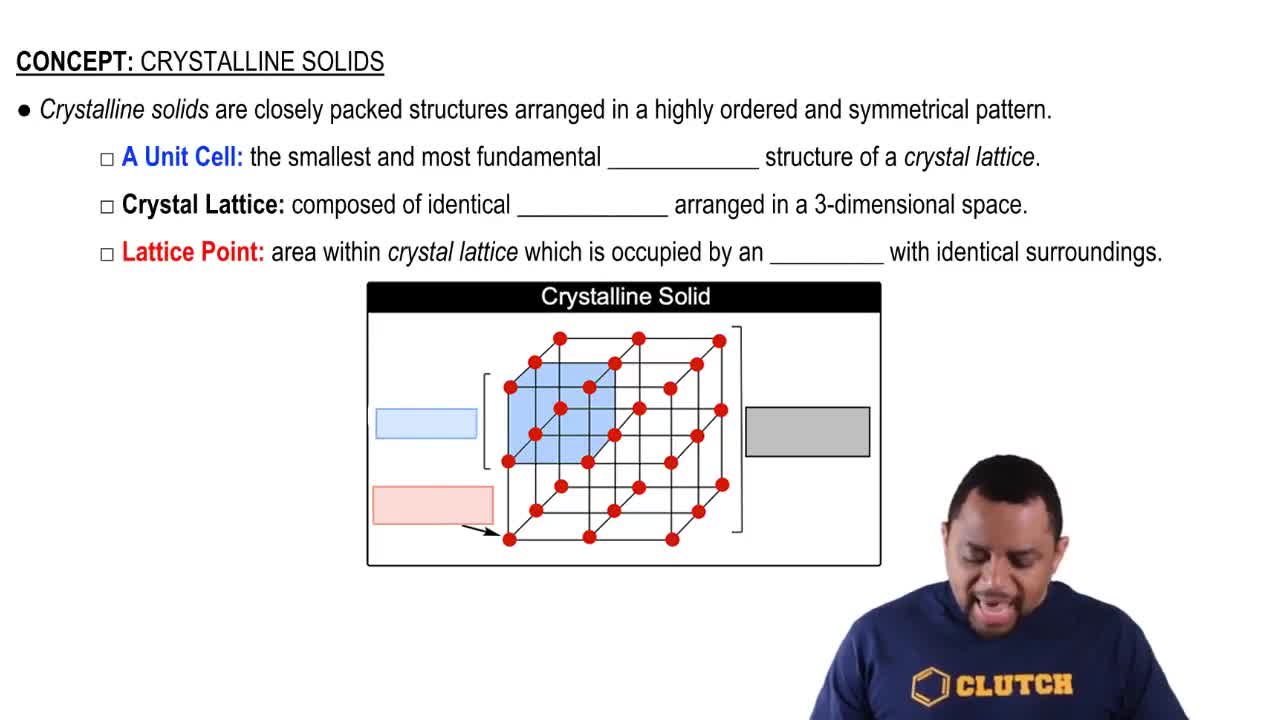
Crystalline Solids Structure
Packing Efficiency
Packing efficiency refers to the fraction of volume in a crystal structure that is occupied by the particles, compared to the total volume of the unit cell. It is a crucial concept in understanding how tightly particles are packed in a lattice. Different packing arrangements, such as close-packed or simple arrangements, lead to varying packing efficiencies, influencing the physical properties of the material.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Cubic Unit Cells
Related Practice
Textbook Question
927
views
Textbook Question
(b) Now draw a picture that represents an amorphous solid at the atomic level.
685
views
Textbook Question
Two patterns of packing for two different circles of the same size are shown here. For each structure (b) determine the angle between the lattice vectors, g, and determine whether the lattice vectors are of the same length or of different lengths; (i)
(ii)
444
views
Textbook Question
Imagine the primitive cubic lattice. Now imagine grabbing the top of it and stretching it straight up. All angles remain 90. What kind of primitive lattice have you made?
423
views
Textbook Question
Which of the three-dimensional primitive lattices has a unit cell where none of the internal angles is 90? (a) Orthorhombic, (b) hexagonal, (c) rhombohedral, (d) triclinic, (e) both rhombohedral and triclinic.
404
views
Open Question
Besides the cubic unit cell, which other unit cell(s) have edge lengths that are all equal to each other? (a) Orthorhombic, (b) hexagonal, (c) rhombohedral, (d) triclinic, (e) both rhombohedral and triclinic.
