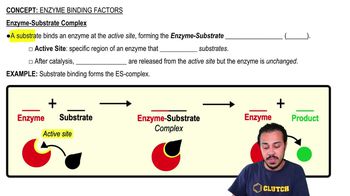
What is a transition state?
a. The shape adopted by an enzyme that has an inhibitory molecule bound at its active site
b. The amount of kinetic energy required for a reaction to proceed
c. The intermediate complex formed as covalent bonds in the reactants are being broken and re-formed during a reaction
d. The enzyme shape after binding an allosteric regulatory molecule