Back
BackProblem 1
What does species richness refer to? Select True or False for each statement. T/F the number of species in an area T/F the evenness of species in an area T/F the functional diversity of a species in an area T/F the phylogenetic diversity of species in an area
Problem 2
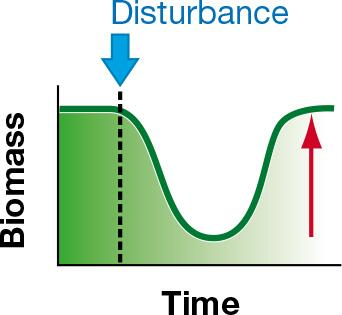
What community property does the red arrow in the model represent? a. high resilience b. low resistance c. high resistance
Problem 3
What is a biodiversity “hotspot”?
a. an area where an all-taxon survey is under way
b. a habitat with high NPP
c. an area with high species richness and high threat to those species
Problem 4
What does ecosystem service refer to? Select True or False for each statement.
T/FBenefits that humans derive from organisms and ecosystems.
T/FBenefits that non-human animals derive from their prey.
Problem 5
Why is the common phrase 'humans and animals' not accurate in biology? Suggest one way that a more scientific outlook could boost conservation efforts.
Problem 6
Biologists claim that the all-taxa survey now under way at the Great Smoky Mountains National Park in the United States will improve their ability to estimate the total number of species living today. Discuss the benefits and limitations that this data set will provide in understanding the extent of global biodiversity.
Problem 7
Some biologists prefer to focus efforts on preserving endangered species while others prefer to focus on preserving ecosystems. What is your advice to biologists, based on the evidence from this chapter?
Problem 8
Explain why the construction of wildlife corridors can help maintain genetic diversity in a fragmented landscape.
Problem 9
Suppose that record snows blanket your campus this winter. Your friend says this is proof that global warming isn't really occurring. What is the flaw in your friend's logic? a. The average temperature of the Earth is not actually increasing. b. Global warming refers to temperatures, but snow is a type of precipitation. c. While the average global temperature is increasing, local temperatures and precipitation (weather) will vary. d. Your friend is confusing global warming and global climate change.
Problem 9
The population size of mountain pine beetles in the American Northwest has long been held in check by freezing temperatures during the winters. As winters warm, populations of pine beetles are increasing, killing whitebark pine forest. Grizzly bears rely on the nuts of whitebark pine trees. Do you think climate change is affecting the fitness of the grizzly bear population?
a. No, because climate change is affecting the beetles, not the bears.
b. Yes, because climate change is decreasing the food supply of the bears, which means they will be less strong.
c. Yes, because climate change is decreasing the food supply of the bears, which is likely to reduce their ability to survive or reproduce.
Problem 10
The maps shown here chronicle the loss of old-growth forest (more than 200 years old) that occurred in the United States. In your opinion, under what conditions is it ethical for conservationists who live in the United States to lobby government officials in Brazil, Indonesia, and other tropical countries to slow the rate of loss of old-growth forest?

Problem 10
During the Carboniferous period, plant growth was extensive but rates of decomposition slowed (probably due to the formation of vast, oxygen-poor swamp habitats). As a result, large amounts of biomass accumulated in terrestrial environments (much of this biomass is now coal). The fossil record indicates that atmospheric oxygen increased, atmospheric carbon dioxide decreased, and global temperatures dropped. Explain why.
Problem 10
Human impacts such as habitat destruction, climate change, and pollution are causing a rapid decline in insect diversity. Pose an argument for why conservation efforts to preserve plant diversity, like Homegrown National Park, are essential for conserving insect diversity.
Problem 11
Scientists around the world are collaborating to understand how deforestation, climate change, and natural processes will interact to affect one of the most productive and biodiverse ecosystems on Earth. a. temperate forest b. tropical dry forest c. tropical grassland d. tropical wet forest
Problem 11
Do you drink coffee? A lot of people do—coffee is a major tropical crop, valued at over $100 billion per year. The most popular species of coffee, Coffea arabica, originated in Africa and is now planted extensively in Central and South America. The pest called the coffee berry borer beetle (Hypothenemus hampeii) moved along with the coffee and is a major problem for coffee farmers, sometimes destroying half of the coffee crop in mature plantations. Based on what you have learned in this chapter about global trends in terrestrial ecosystems, what is currently the largest threat to the wet tropical forests in Central America? a. habitat destruction, such as the clearing of forests for coffee plantations b. exotic species, such as the introduction of coffee berry borers c. pollution, such as the use of pesticides in coffee plantations d. climate change, such as changes in precipitation patterns
Problem 12
Do you drink coffee? A lot of people do—coffee is a major tropical crop, valued at over $100 billion per year. The most popular species of coffee, Coffea arabica, originated in Africa and is now planted extensively in Central and South America. The pest called the coffee berry borer beetle (Hypothenemus hampeii) moved along with the coffee and is a major problem for coffee farmers, sometimes destroying half of the coffee crop in mature plantations. Pesticides are generally ineffective in killing coffee berry borers. Ecologist Daniel Karp and colleagues conducted a study in Costa Rica to determine if natural predators like birds reduce the beetle population. The researchers selected 12 control plots and used nets to exclude birds from 12 similar treatment plots. What is the take-home message of the graph? (Remember, * means P 6 0.05)

Problem 12
Scientists around the world are collaborating to understand how deforestation, climate change, and natural processes will interact to affect one of the most productive and biodiverse ecosystems on Earth. Select True or False for each statement about the effects of clear-cutting on the Amazon rain forest, then explain your reasoning. T/F Nutrient export is likely to decline. T/F Atmospheric CO2 is likely to decline. T/F Soil moisture is likely to decline. T/F Species diversity is likely to decline.
Problem 13
Do you drink coffee? A lot of people do—coffee is a major tropical crop, valued at over $100 billion per year. The most popular species of coffee, Coffea arabica, originated in Africa and is now planted extensively in Central and South America. The pest called the coffee berry borer beetle (Hypothenemus hampeii) moved along with the coffee and is a major problem for coffee farmers, sometimes destroying half of the coffee crop in mature plantations. Look at the graph.

Why did the researchers bother to collect data from the coffee shrubs before adding the nets to treatment plots to exclude birds?

Problem 13
Scientists around the world are collaborating to understand how deforestation, climate change, and natural processes will interact to affect one of the most productive and biodiverse ecosystems on Earth. Researchers have measured the effects of periodic forest fires on primary productivity in Amazon rain forest plots, comparing years with average precipitation and years with severe drought. Propose which controls would be necessary for such studies.
Problem 14
Scientists around the world are collaborating to understand how deforestation, climate change, and natural processes will interact to affect one of the most productive and biodiverse ecosystems on Earth. This box-and-arrow model summarizes some of the feedback links observed in the Amazon rain forest. Select True or False for the statements that follow, based on whether they are represented by the model. (Note that the boxes and arrows in this model are used differently than those in the nutrient cycle models). T/F The burning of fossil fuels increases atmospheric CO2. T/F Tree growth reduces atmospheric CO2. T/F The death of trees promotes the invasion of grasses. T/F An increase in CO2 increases the frequency of droughts. T/F Drought increases the frequency of forest fires.

Problem 14
Do you drink coffee? A lot of people do—coffee is a major tropical crop, valued at over $100 billion per year. The most popular species of coffee, Coffea arabica, originated in Africa and is now planted extensively in Central and South America. The pest called the coffee berry borer beetle (Hypothenemus hampeii) moved along with the coffee and is a major problem for coffee farmers, sometimes destroying half of the coffee crop in mature plantations. The abundance of birds and other predators of borer beetles depends on how much natural forest is left within and around the coffee plantations. What is the approximate percentage increase in borer predators per hectare if forest cover is doubled from 15 to 30 percent?

Problem 15
Scientists around the world are collaborating to understand how deforestation, climate change, and natural processes will interact to affect one of the most productive and biodiverse ecosystems on Earth. Many studies have raised the concern that positive feedback loops among numerous variables in the Amazon will cause an ecosystem tipping point—a rapid and irreversible transition from forest to grassland. Use the model in Question 14 as a tool to summarize a possible sequence of effects that could cause a transition from forest to grassland.
Problem 15
Do you drink coffee? A lot of people do—coffee is a major tropical crop, valued at over $100 billion per year. The most popular species of coffee, Coffea arabica, originated in Africa and is now planted extensively in Central and South America. The pest called the coffee berry borer beetle (Hypothenemus hampeii) moved along with the coffee and is a major problem for coffee farmers, sometimes destroying half of the coffee crop in mature plantations. Draw a simple model to compare the relative species richness and species diversity of these two coffee plantations: one is clear-cut and planted with only coffee shrubs, the other retains some natural forest. For symbols, use a few letters to represent different species of plants and a few numbers to represent different species of animals in a square 1-ha plot.
Problem 15
This study suggests a form of sentience (the capacity to experience feelings and sensations) in bumble bees. How might these findings impact conservation policies?
Problem 16
Do you drink coffee? A lot of people do—coffee is a major tropical crop, valued at over $100 billion per year. The most popular species of coffee, Coffea arabica, originated in Africa and is now planted extensively in Central and South America. The pest called the coffee berry borer beetle (Hypothenemus hampeii) moved along with the coffee and is a major problem for coffee farmers, sometimes destroying half of the coffee crop in mature plantations. Evaluate this statement: Leaving some natural forest in and around coffee plantations is a 'win-win' situation—a win for ecosystems and a win for farmers.
Problem 16
Scientists around the world are collaborating to understand how deforestation, climate change, and natural processes will interact to affect one of the most productive and biodiverse ecosystems on Earth. Journalists must be concise when reporting science news. Why might journalists and the public struggle to understand and discuss ecosystems ecology and global warming?