Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Myofilament Composition
Myofilaments are the contractile proteins in muscle fibers, primarily categorized into thick and thin filaments. Thick filaments are primarily composed of myosin, while thin filaments consist mainly of actin, along with regulatory proteins such as troponin and tropomyosin. Understanding the distinct compositions of these filaments is crucial for analyzing muscle contraction mechanisms.
Recommended video:
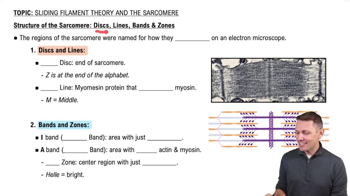
Z Disc and Sarcomere Structure
The Z disc is a structural component of the sarcomere, the basic unit of muscle contraction. Thin filaments attach to the Z disc, while thick filaments are situated in the center of the sarcomere. This arrangement is essential for the sliding filament theory, which explains how muscle contraction occurs through the interaction of thick and thin filaments.
Recommended video:
Structure of the Sarcomere: Bands, Zones, Discs & Lines
Role of ATP in Muscle Contraction
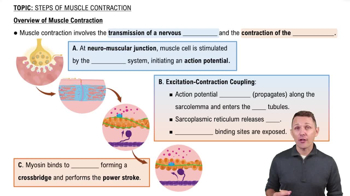
ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is vital for muscle contraction as it provides the energy required for the myosin heads to bind to actin and perform the power stroke. Thick filaments contain ATPases, enzymes that hydrolyze ATP to release energy. This energy is crucial for muscle contraction and relaxation, making the understanding of ATP's role essential in muscle physiology.
Recommended video:
Overview of Muscle Contraction