Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Twitch
A twitch is a single, brief contraction of a muscle fiber or a group of muscle fibers in response to a single stimulus. It consists of a latent period, a contraction phase, and a relaxation phase. This concept is fundamental in understanding muscle physiology and how muscles respond to stimuli.
Recommended video:
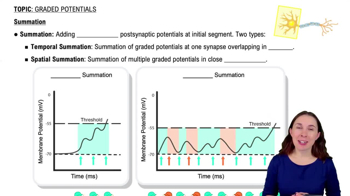
Temporal Summation
Temporal summation occurs when multiple stimuli are applied to a muscle in rapid succession, leading to an increased force of contraction. This happens because the muscle does not have enough time to fully relax between stimuli, resulting in a stronger overall contraction. It is essential for understanding how muscles can generate greater force under certain conditions.
Recommended video:
Motor Unit Summation
Motor unit summation refers to the recruitment of additional motor units to increase muscle contraction strength. When a muscle is stimulated, not all motor units are activated simultaneously; instead, they are recruited based on the strength of the stimulus. This concept is crucial for understanding how muscles can vary their force output depending on the demands placed on them.
Recommended video: