Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Isometric Contraction
Isometric contractions occur when a muscle generates force without changing its length. This type of contraction is characterized by the muscle maintaining a constant length while producing tension, which is essential in stabilizing joints and maintaining posture.
Recommended video:
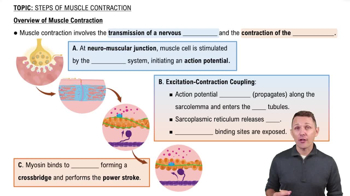
Overview of Muscle Contraction
Muscle Tension
Muscle tension refers to the force exerted by a muscle when it contracts. In isometric contractions, muscle tension increases without any change in muscle length, allowing for strength development without movement, which is particularly useful in resistance training.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Muscles and Muscle Tissue Example 1
Resistance Training
Resistance training involves exercises that improve strength and endurance by working against a force. Isometric contractions are often incorporated into resistance training routines, as they help build muscle strength and stability without the need for dynamic movement.
Recommended video:
Altering Resistance in Blood Vessels
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance