Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Muscle Contraction Types
Muscle contractions can be categorized into different types, including twitch, tetanus, and summation. A twitch is a single, brief contraction of a muscle fiber, while tetanus refers to a sustained contraction resulting from rapid stimulation. Understanding these types is crucial for distinguishing between them in physiological contexts.
Recommended video:
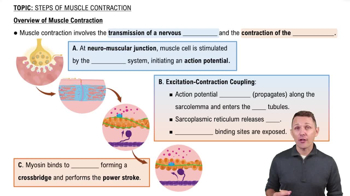
Overview of Muscle Contraction
Fused Tetanus
Fused tetanus occurs when a muscle is stimulated at a high frequency, leading to a sustained contraction without any relaxation between stimuli. This results in a smooth and continuous contraction, which is essential for maintaining muscle tone and performing prolonged activities. It is a key concept in understanding muscle physiology and performance.
Recommended video:
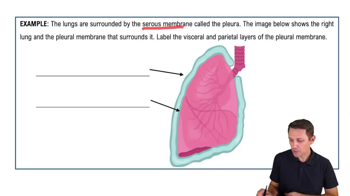
Organization of the Body: Serous Membranes Example 1
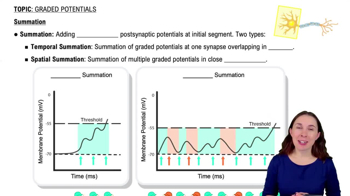
Summation
Summation refers to the process where multiple stimuli are applied to a muscle in quick succession, leading to an increase in the strength of contraction. Temporal summation involves increasing the frequency of stimulation, while multiple motor unit summation involves recruiting more muscle fibers. Both processes are vital for understanding how muscles generate force and respond to different levels of activity.
Recommended video: