Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
T Tubules
T tubules, or transverse tubules, are extensions of the muscle cell membrane that penetrate into the muscle fiber. They play a crucial role in conducting electrical impulses, or action potentials, from the surface of the muscle cell deep into its interior, ensuring that the entire muscle fiber contracts simultaneously.
Recommended video:
T Dependent & T Independent Antigens
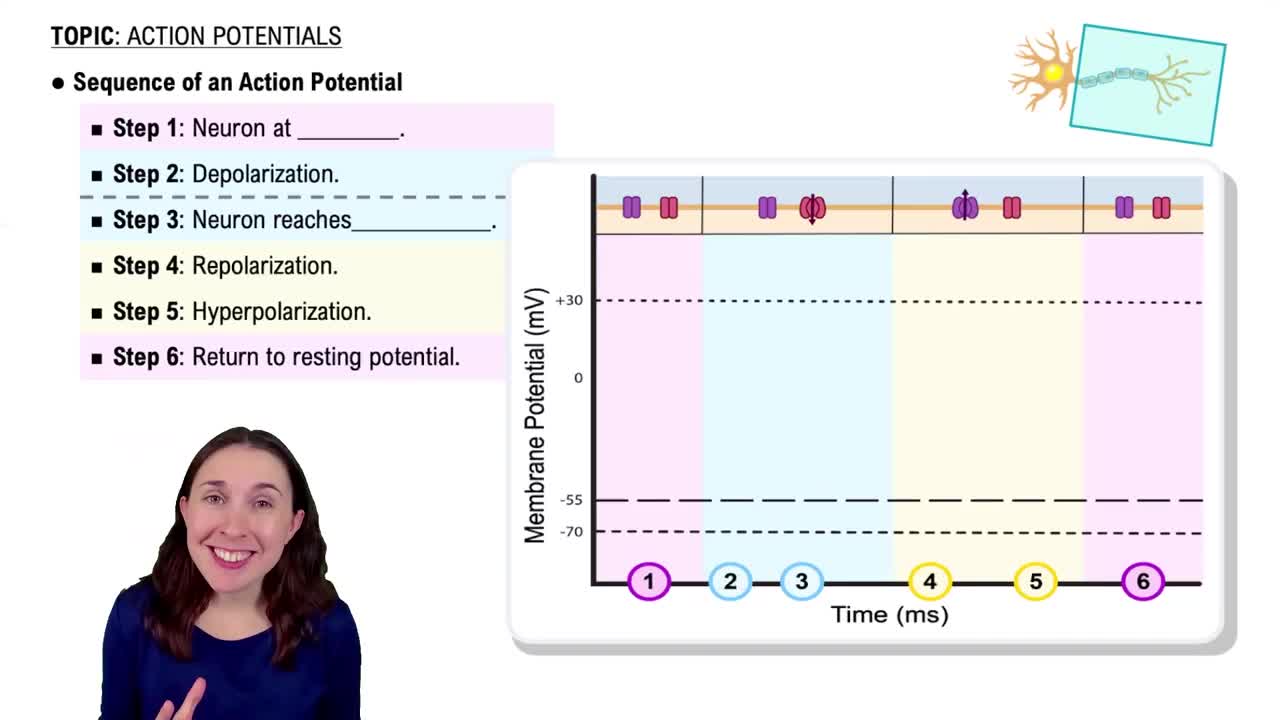
Action Potential
An action potential is a rapid change in the electrical charge across a cell membrane, which occurs when a neuron or muscle cell is stimulated. In muscle contraction, the action potential travels along the T tubules, triggering the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which is essential for muscle contraction.
Recommended video:
Calcium Ions (Ca²⁺)
Calcium ions (Ca²⁺) are vital signaling molecules in muscle contraction. When the action potential reaches the T tubules, it stimulates the release of Ca²⁺ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum into the cytoplasm, initiating the interaction between actin and myosin filaments, which leads to muscle contraction.
Recommended video:
Ions - Sodium and Potassium Example 3
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance