Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
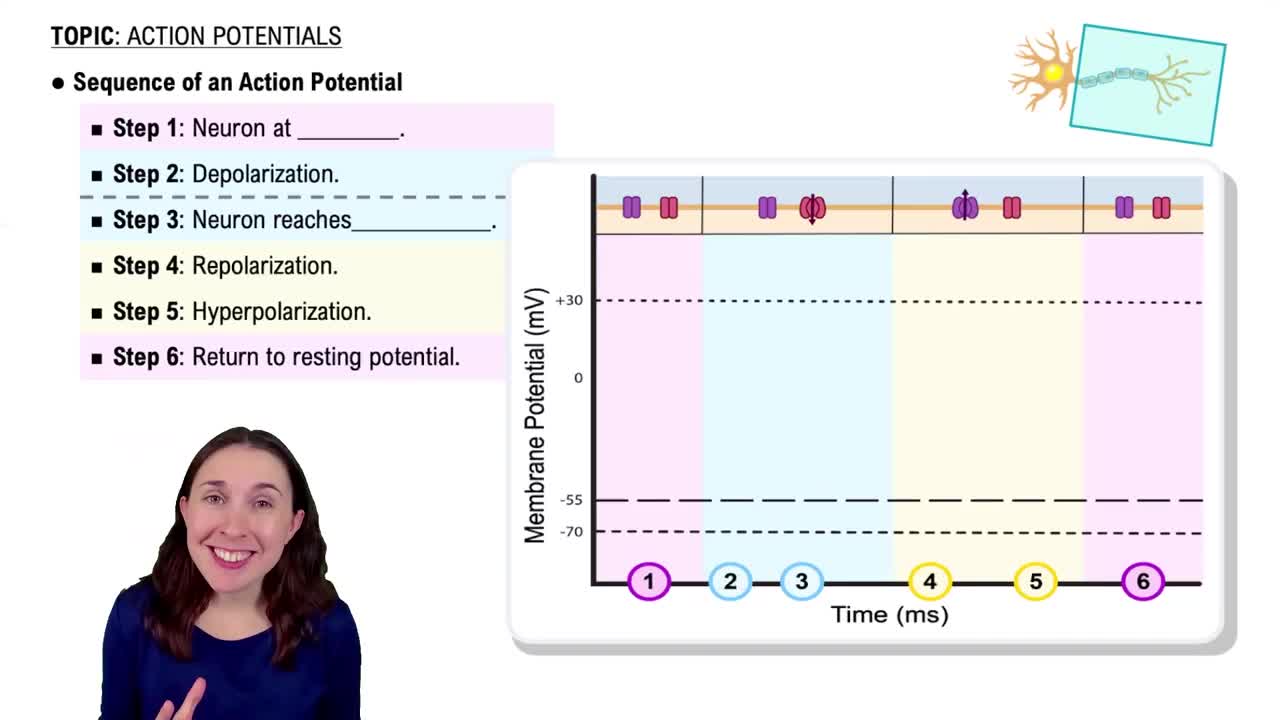
Action Potential
An action potential is a rapid, temporary change in the electrical membrane potential of a cell, particularly in neurons and muscle cells. It occurs when a stimulus causes the membrane to depolarize, leading to the opening of voltage-gated ion channels. This process is essential for the transmission of signals in the nervous system and the contraction of muscle fibers.
Recommended video:
Ion Channels
Ion channels are specialized proteins embedded in the cell membrane that allow specific ions to pass in and out of the cell. During an action potential, sodium (Na+) channels open first, allowing sodium ions to flow into the cell, which contributes to depolarization. Other ion channels, such as potassium (K+) and calcium (Ca2+), play roles in repolarization and muscle contraction.
Recommended video:
Ions - Sodium and Potassium Example 3
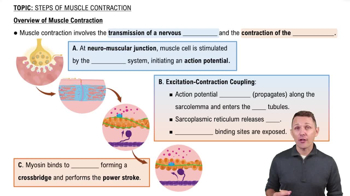
Skeletal Muscle Contraction
Skeletal muscle contraction is initiated by the influx of calcium ions into the muscle cell, which triggers the interaction between actin and myosin filaments. However, during the generation of an action potential, sodium ions are primarily responsible for depolarizing the membrane. Understanding the role of these ions is crucial for comprehending how muscle contractions are controlled and executed.
Recommended video:
Overview of Muscle Contraction
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance