Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Aerobic Exercise
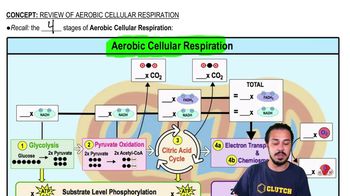
Aerobic exercise refers to physical activities that rely on the aerobic energy-generating process, which uses oxygen to fuel the body during prolonged activities. This type of exercise, such as running or cycling, enhances cardiovascular endurance and promotes overall health by improving the efficiency of the heart and lungs.
Recommended video:
Review of Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Muscle Adaptations
Muscle adaptations are physiological changes that occur in response to regular aerobic training. These adaptations include an increase in the number of capillaries, mitochondria, and myoglobin in muscle cells, which enhance oxygen delivery and utilization, ultimately improving endurance and performance.
Recommended video:
Hypertrophy vs. Endurance Training
Hypertrophy refers to the increase in muscle size and strength, typically associated with resistance training rather than aerobic exercise. While aerobic exercise can lead to some muscle adaptations, it primarily focuses on endurance rather than significantly increasing the size of existing muscle cells, which is why options related to hypertrophy are less likely to be a result of aerobic training.
Recommended video:
Passive vs. Active Transport
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance